Abstract
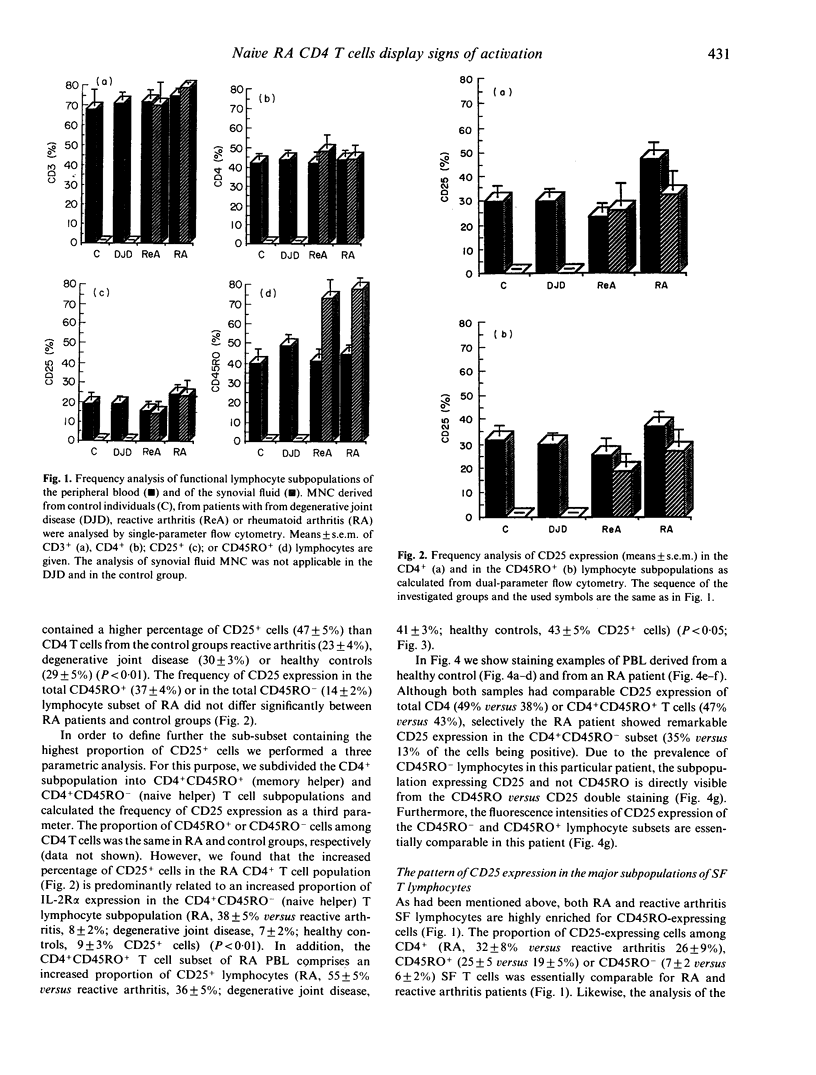
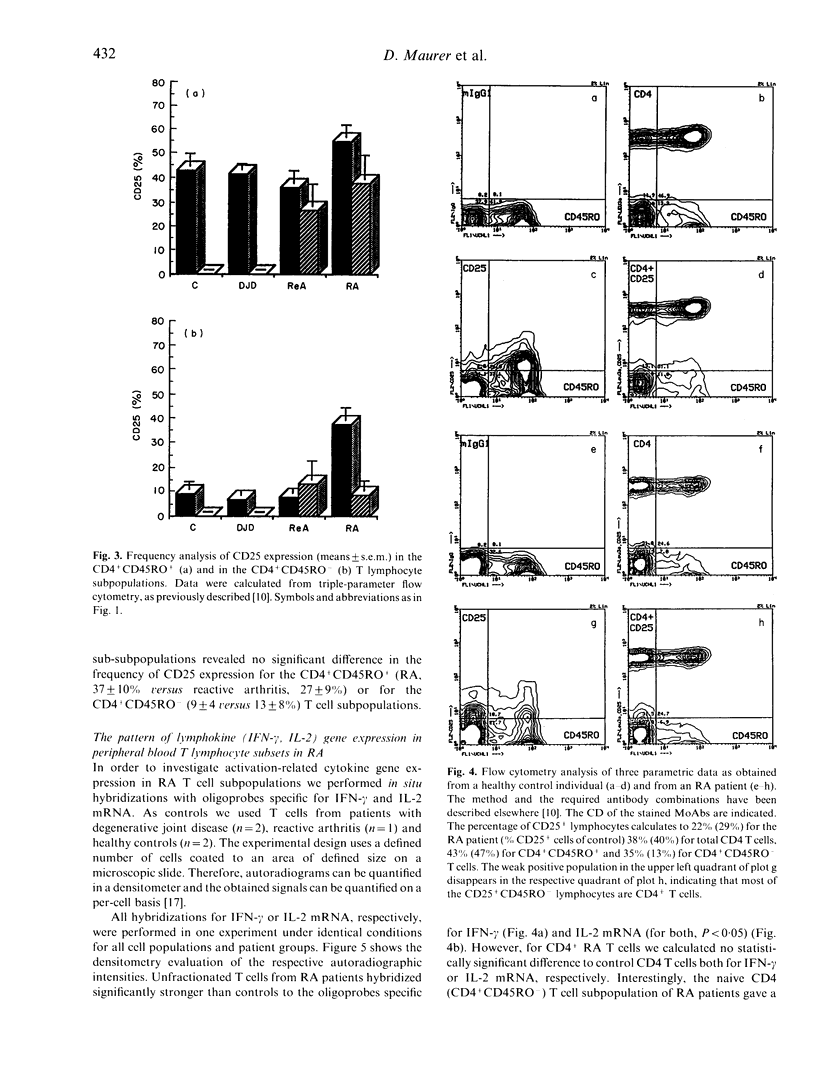
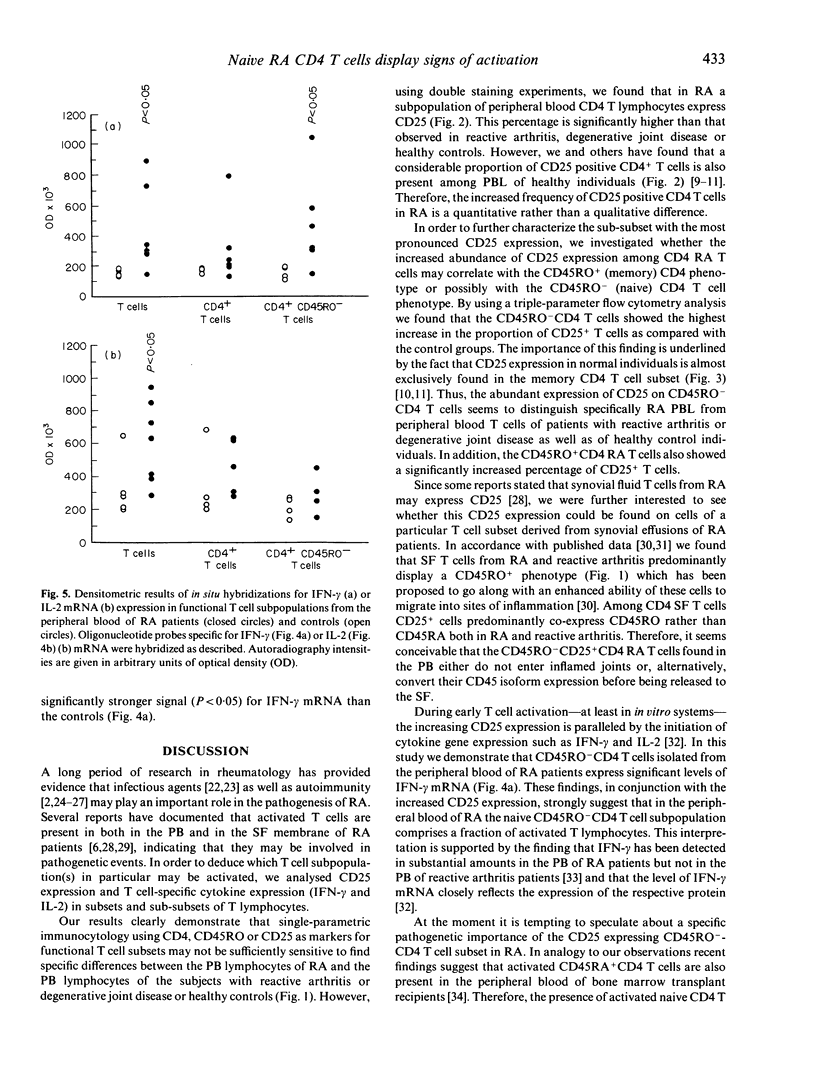
We have investigated whether T cell activation in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) preferentially engages distinct T cell subpopulations in the peripheral blood (PB) and in the synovial fluid. We found that CD25 expression was enhanced among PB CD4 T cells of RA patients as compared with CD4 cells of patients with reactive arthritis, degenerative joint disease or of healthy controls. Within the CD4 T lymphocytes subset we found that the CD45RO- (naive) cells selectively in RA displayed higher levels of CD25 protein and of interferon-gamma mRNA expression when compared with the respective subset of all other investigated groups. These results show that in the PB of RA, but not in the PB of the other arthropathies or healthy controls, CD45RO-CD4 T lymphocytes exist which display well-defined signs of activation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akbar A. N., Terry L., Timms A., Beverley P. C., Janossy G. Loss of CD45R and gain of UCHL1 reactivity is a feature of primed T cells. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 1;140(7):2171–2178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beverley P. C. Human T cell subsets. Immunol Lett. 1987 Apr;14(4):263–267. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(87)90001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchan G., Barrett K., Fujita T., Taniguchi T., Maini R., Feldmann M. Detection of activated T cell products in the rheumatoid joint using cDNA probes to Interleukin-2 (IL-2) IL-2 receptor and IFN-gamma. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Feb;71(2):295–301. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burmester G. R., Jahn B., Gramatzki M., Zacher J., Kalden J. R. Activated T cells in vivo and in vitro: divergence in expression of Tac and Ia antigens in the nonblastoid small T cells of inflammation and normal T cells activated in vitro. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1230–1234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cush J. J., Lipsky P. E. Phenotypic analysis of synovial tissue and peripheral blood lymphocytes isolated from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Oct;31(10):1230–1238. doi: 10.1002/art.1780311003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery P., Wood N., Gentry K., Stockman A., Mackay I. R., Bernard O. High-affinity interleukin-2 receptors on blood lymphocytes are decreased during active rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Sep;31(9):1176–1181. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firestein G. S., Alvaro-Gracia J. M., Maki R., Alvaro-Garcia J. M. Quantitative analysis of cytokine gene expression in rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol. 1990 May 1;144(9):3347–3353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firestein G. S., Tsai V., Zvaifler N. J. Cellular immunity in the joints of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other forms of chronic synovitis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1987 Aug;13(2):191–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabstein K., Dower S., Gillis S., Urdal D., Larsen A. Expression of interleukin 2, interferon-gamma, and the IL 2 receptor by human peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4503–4508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. W., Leung D. W., Pennica D., Yelverton E., Najarian R., Simonsen C. C., Derynck R., Sherwood P. J., Wallace D. M., Berger S. L. Expression of human immune interferon cDNA in E. coli and monkey cells. Nature. 1982 Feb 11;295(5849):503–508. doi: 10.1038/295503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovdenes J., Gaudernack G., Kvien T. K., Egeland T. Expression of activation markers on CD4+ and CD8+ cells from synovial fluid, synovial tissue, and peripheral blood of patients with inflammatory arthritides. Scand J Immunol. 1989 Jun;29(6):631–639. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1989.tb01167.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janossy G., Panayi G., Duke O., Bofill M., Poulter L. W., Goldstein G. Rheumatoid arthritis: a disease of T-lymphocyte/macrophage immunoregulation. Lancet. 1981 Oct 17;2(8251):839–842. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91107-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jasin H. E. Abnormalities of immune regulation in the connective tissue diseases. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Aug;13(1 Suppl 1):94–98. doi: 10.1016/0049-0172(83)90026-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasky H. P., Bauer K., Pope R. M. Increased helper inducer and decreased suppressor inducer phenotypes in the rheumatoid joint. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Jan;31(1):52–59. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer D., Felzmann T., Knapp W. A single laser flow cytometry method to evaluate the binding of three antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1990 Dec 31;135(1-2):43–47. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90254-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDermott M., McDevitt H. The immunogenetics of rheumatic diseases. Bull Rheum Dis. 1988;38(1):1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi Y., Takeshita T., Nagata K., Mori S., Sugamura K. Differential expression of the IL-2 receptor subunits, p55 and p75 on various populations of primary peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 1;143(11):3548–3555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips P. E. Evidence implicating infectious agents in rheumatoid arthritis and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1988 Jan-Mar;6(1):87–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitzalis C., Kingsley G., Lanchbury J. S., Murphy J., Panayi G. S. Expression of HLA-DR, DQ and DP antigens and interleukin-2 receptor on synovial fluid T lymphocyte subsets in rheumatoid arthritis: evidence for "frustrated" activation. J Rheumatol. 1987 Aug;14(4):662–666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitzalis C., Kingsley G., Murphy J., Panayi G. Abnormal distribution of the helper-inducer and suppressor-inducer T-lymphocyte subsets in the rheumatoid joint. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1987 Nov;45(2):252–258. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(87)90040-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulter L. W., Duke O., Panayi G. S., Hobbs S., Raftery M. J., Janossy G. Activated T lymphocytes of the synovial membrane in rheumatoid arthritis and other arthropathies. Scand J Immunol. 1985 Dec;22(6):683–690. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1985.tb01931.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders M. E., Makgoba M. W., Shaw S. Human naive and memory T cells: reinterpretation of helper-inducer and suppressor-inducer subsets. Immunol Today. 1988 Jul-Aug;9(7-8):195–199. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91212-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxne T., Palladino M. A., Jr, Heinegård D., Talal N., Wollheim F. A. Detection of tumor necrosis factor alpha but not tumor necrosis factor beta in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid and serum. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Aug;31(8):1041–1045. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz M., Weber S., Seifert J. M., Holter W. A simple and rapid slide blot method to quantify cytokine-mRNA in small numbers of lymphocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1991 Dec 15;145(1-2):27–32. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(91)90307-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamenkovic I., Stegagno M., Wright K. A., Krane S. M., Amento E. P., Colvin R. B., Duquesnoy R. J., Kurnick J. T. Clonal dominance among T-lymphocyte infiltrates in arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1179–1183. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart J. M., Townes A. S., Kang A. H. Collagen autoimmune arthritis. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:199–218. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.001215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symons J. A., Wood N. C., Di Giovine F. S., Duff G. W. Soluble IL-2 receptor in rheumatoid arthritis. Correlation with disease activity, IL-1 and IL-2 inhibition. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 15;141(8):2612–2618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taga K., Kasahara Y., Yachie A., Miyawaki T., Taniguchi N. Preferential expression of IL-2 receptor subunits on memory populations within CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. Immunology. 1991 Jan;72(1):15–19. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T., Matsui H., Fujita T., Takaoka C., Kashima N., Yoshimoto R., Hamuro J. Structure and expression of a cloned cDNA for human interleukin-2. Nature. 1983 Mar 24;302(5906):305–310. doi: 10.1038/302305a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venables P. J. Infection and rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 1989 Jun;1(1):15–20. doi: 10.1097/00002281-198901010-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young W. S., 3rd, Bonner T. I., Brann M. R. Mesencephalic dopamine neurons regulate the expression of neuropeptide mRNAs in the rat forebrain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9827–9831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


