Abstract
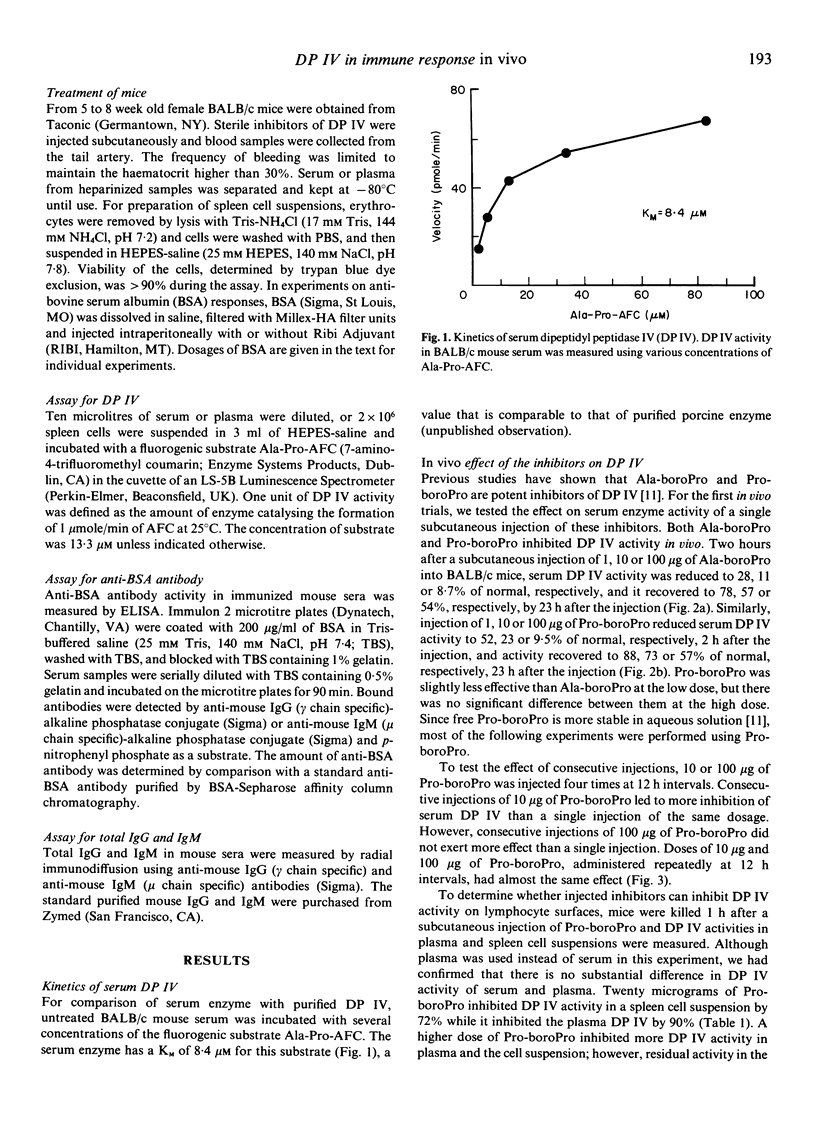
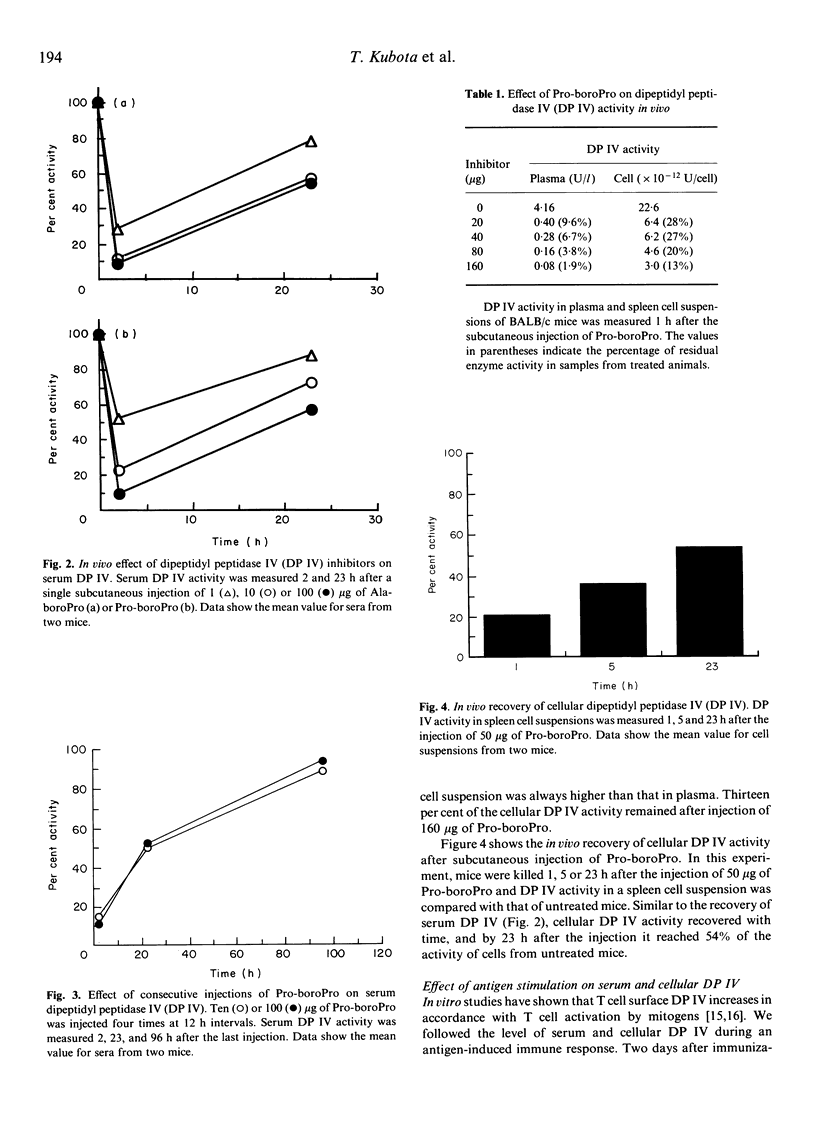
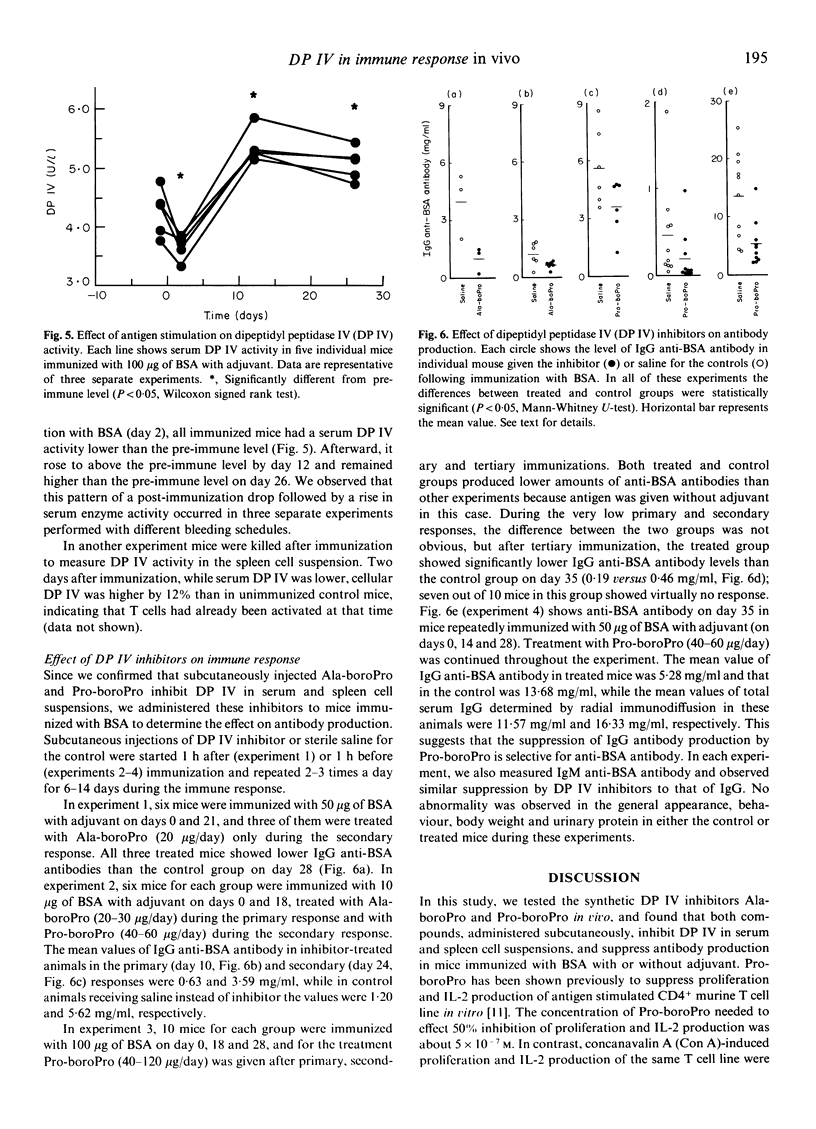
Dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DP IV) is a serine protease that selectively cleaves X-Pro dipeptides from polypeptides and proteins. Among blood cells, this enzyme occurs preferentially on the surface of CD4+ T cells and the amount of enzyme activity increases with T cell activation. In previous work, two potent and specific peptidyl-boronic acid inhibitors of DP IV, Ala-boroPro and Pro-boroPro, were synthesized and Pro-boroPro was shown to suppress antigen-specific proliferative responses of T cells in vitro. In this study, we tested the in vivo effects of these inhibitors. Subcutaneous injection of Ala-boroPro or Pro-boroPro into BALB/c mice inhibited DP IV activity in serum and spleen cell suspensions. Repeated injections of more than 10 micrograms of Ala-boroPro or Pro-boroPro at 12 h intervals maintained in vivo DP IV activity at less than 30% of the normal level. Repeated injections of the inhibitors during the primary, secondary or tertiary immune response to bovine serum albumin (BSA) reduced anti-BSA antibody production. Without inhibitor, immunization with BSA was followed by a temporary decrease in serum DP IV activity and then by enhanced serum enzyme activity after several days. These results provide the first direct evidence that DP IV plays an important role in immune response in vivo.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews C., Crockard A. D., San Miguel J. F., Catovsky D. Dipeptidylaminopeptidase IV (DAP IV) in B- and T-cell leukaemias. Clin Lab Haematol. 1985;7(4):359–368. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2257.1985.tb00050.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton R. W., Prendergast J., Kennedy C. A. Binding of the T cell activation monoclonal antibody Ta1 to dipeptidyl peptidase IV. J Leukoc Biol. 1990 Oct;48(4):291–296. doi: 10.1002/jlb.48.4.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dang N. H., Torimoto Y., Deusch K., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. Comitogenic effect of solid-phase immobilized anti-1F7 on human CD4 T cell activation via CD3 and CD2 pathways. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 1;144(11):4092–4100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dang N. H., Torimoto Y., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. Human CD4 helper T cell activation: functional involvement of two distinct collagen receptors, 1F7 and VLA integrin family. J Exp Med. 1990 Aug 1;172(2):649–652. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.2.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer B. A novel pathway of human T cell activation via a 103 kD T cell activation antigen. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 1;138(5):1346–1350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flentke G. R., Munoz E., Huber B. T., Plaut A. G., Kettner C. A., Bachovchin W. W. Inhibition of dipeptidyl aminopeptidase IV (DP-IV) by Xaa-boroPro dipeptides and use of these inhibitors to examine the role of DP-IV in T-cell function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1556–1559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruber M., Scholz W., Flad H. D. Influence of human T lymphocytes identified by antibodies to dipeptidyl peptidase IV on differentiation of human B lymphocytes stimulated with Staphylococcus aureus Cowan I and pokeweed mitogen. Cell Immunol. 1988 May;113(2):423–434. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(88)90039-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegen M., Niedobitek G., Klein C. E., Stein H., Fleischer B. The T cell triggering molecule Tp103 is associated with dipeptidyl aminopeptidase IV activity. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 15;144(8):2908–2914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hino M., Nagatsu T., Kakumu S., Okuyama S., Yoshii Y., Nagatsu I. Glycylprolyl beta-naphthylamidase activity in human serum. Clin Chim Acta. 1975 Jul 9;62(1):5–11. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(75)90273-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopsu-Havu V. K., Glenner G. G. A new dipeptide naphthylamidase hydrolyzing glycyl-prolyl-beta-naphthylamide. Histochemie. 1966;7(3):197–201. doi: 10.1007/BF00577838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettner C. A., Bone R., Agard D. A., Bachovchin W. W. Kinetic properties of the binding of alpha-lytic protease to peptide boronic acids. Biochemistry. 1988 Oct 4;27(20):7682–7688. doi: 10.1021/bi00420a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khalaf M. R., Aqel N. M., Hayhoe F. G. Histochemistry of dipeptidyl aminopeptidase (DAP) II and IV in reactive lymphoid tissues and malignant lymphoma. J Clin Pathol. 1987 May;40(5):480–485. doi: 10.1136/jcp.40.5.480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lojda Z. Studies on glycyl-proline naphthylamidase. I. Lymphocytes. Histochemistry. 1977 Dec 28;54(4):299–309. doi: 10.1007/BF00508273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto C., Torimoto Y., Levinson G., Rudd C. E., Schrieber M., Dang N. H., Letvin N. L., Schlossman S. F. 1F7, a novel cell surface molecule, involved in helper function of CD4 cells. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 1;143(11):3430–3439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oya H., Nagatsu I., Nagatsu T. Purification and properties of glycylprolyl -naphthylamidase in human submaxillary gland. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 28;258(2):591–599. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90251-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholz W., Mentlein R., Heymann E., Feller A. C., Ulmer A. J., Flad H. D. Interleukin 2 production by human T lymphocytes identified by antibodies to dipeptidyl peptidase IV. Cell Immunol. 1985 Jun;93(1):199–211. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90400-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schön E., Ansorge S. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV in the immune system. Cytofluorometric evidence for induction of the enzyme on activated T lymphocytes. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1990 Aug;371(8):699–705. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1990.371.2.699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schön E., Demuth H. U., Eichmann E., Horst H. J., Körner I. J., Kopp J., Mattern T., Neubert K., Noll F., Ulmer A. J. Dipeptidyl peptidase IV in human T lymphocytes. Impaired induction of interleukin 2 and gamma interferon due to specific inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase IV. Scand J Immunol. 1989 Feb;29(2):127–132. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1989.tb01108.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schön E., Jahn S., Kiessig S. T., Demuth H. U., Neubert K., Barth A., Von Baehr R., Ansorge S. The role of dipeptidyl peptidase IV in human T lymphocyte activation. Inhibitors and antibodies against dipeptidyl peptidase IV suppress lymphocyte proliferation and immunoglobulin synthesis in vitro. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Dec;17(12):1821–1826. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830171222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson B., Danielsen M., Staun M., Jeppesen L., Norén O., Sjöström H. An amphiphilic form of dipeptidyl peptidase IV from pig small-intestinal brush-border membrane. Purification by immunoadsorbent chromatography and some properties. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Oct 16;90(3):489–498. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12628.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulmer A. J., Mattern T., Feller A. C., Heymann E., Flad H. D. CD26 antigen is a surface dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPPIV) as characterized by monoclonal antibodies clone TII-19-4-7 and 4EL1C7. Scand J Immunol. 1990 Apr;31(4):429–435. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1990.tb02789.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter R., Simmons W. H., Yoshimoto T. Proline specific endo- and exopeptidases. Mol Cell Biochem. 1980 Apr 18;30(2):111–127. doi: 10.1007/BF00227927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


