Abstract
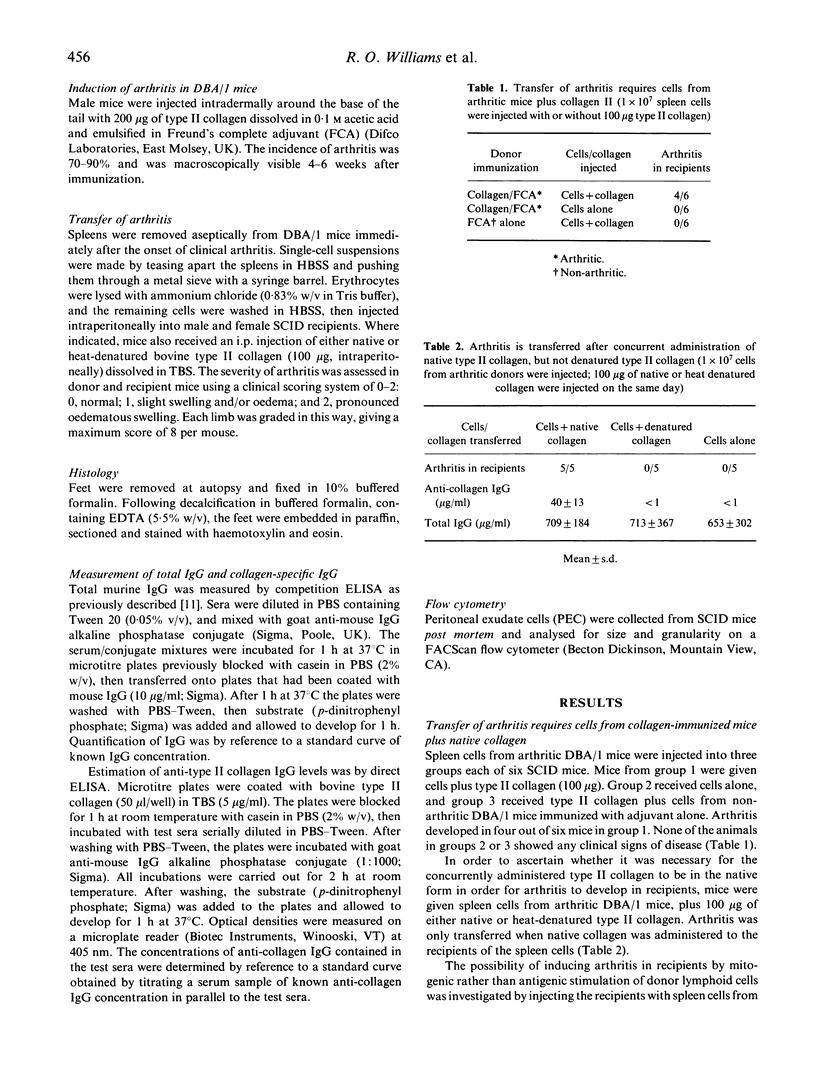
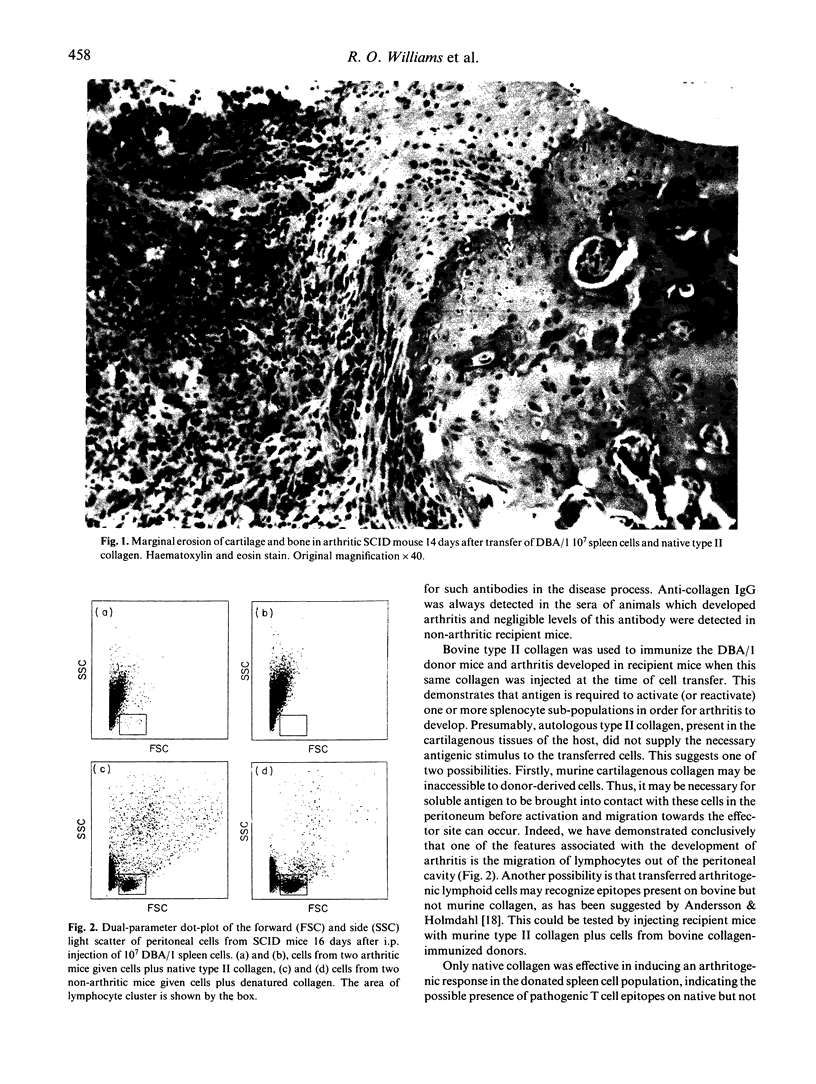
We describe the adoptive transfer of erosive arthritis to an immunodeficient host. Spleen cells from arthritic DBA/1 mice (H-2q), immunized 4-6 weeks previously with bovine type II collagen in adjuvant, were transferred intraperitoneally into SCID mice (H-2d). SCID recipient mice also received native or denatured type II collagen (100 micrograms intraperitoneally) at the time of cell transfer. Arthritis developed in five out of five mice approximately 2 weeks after injection of cells plus native collagen, whereas animals injected with cells plus denatured collagen did not show any clinical or histological evidence of arthritis. The minimum graft size required for successful transfer of arthritis was established at 10(7) DBA/1 spleen cells. Histological examination of the joints of arthritic SCID recipient mice revealed synovitis, fibrosis and erosion of cartilage and underlying bone. Mean circulating levels of anti-type II collagen IgG were found to be significantly higher in mice injected with native collagen than those injected with denatured collagen (40 micrograms/ml and less than 1 microgram/ml, respectively). The ability to transfer collagen-induced arthritis adoptively should facilitate the study of the cellular requirement and pathological mechanisms involved in the induction of this arthropathy.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bosma G. C., Custer R. P., Bosma M. J. A severe combined immunodeficiency mutation in the mouse. Nature. 1983 Feb 10;301(5900):527–530. doi: 10.1038/301527a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brahn E., Trentham D. E. Antigen-specific suppression of collagen arthritis by adoptive transfer of spleen cells. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1984 Apr;31(1):124–131. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(84)90197-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrai I., Henderson B., Knight S. C., Staines N. A. Suppression of collagen type II-induced arthritis by transfer of lymphoid cells from rats immunized with collagen. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Aug;61(2):368–372. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmdahl R., Andersson M., Tarkowski A. Origin of the autoreactive anti-type II collagen response. I. Frequency of specific and multispecific B cells in primed murine lymph nodes. Immunology. 1987 Jul;61(3):369–374. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmdahl R., Jonsson R., Larsson P., Klareskog L. Early appearance of activated CD4+ T lymphocytes and class II antigen-expressing cells in joints of DBA/1 mice immunized with type II collagen. Lab Invest. 1988 Jan;58(1):53–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmdahl R., Klareskog L., Rubin K., Larsson E., Wigzell H. T lymphocytes in collagen II-induced arthritis in mice. Characterization of arthritogenic collagen II-specific T-cell lines and clones. Scand J Immunol. 1985 Sep;22(3):295–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1985.tb01884.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hom J. T., Stuart J. M., Chiller J. M. Murine T cells reactive to type II collagen. I. Isolation of lines and clones and characterization of their antigen-induced proliferative responses. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 1;136(3):769–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janossy G., Panayi G., Duke O., Bofill M., Poulter L. W., Goldstein G. Rheumatoid arthritis: a disease of T-lymphocyte/macrophage immunoregulation. Lancet. 1981 Oct 17;2(8251):839–842. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91107-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakimoto K., Katsuki M., Hirofuji T., Iwata H., Koga T. Isolation of T cell line capable of protecting mice against collagen-induced arthritis. J Immunol. 1988 Jan 1;140(1):78–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakimoto K., Koga T., Onoue K. Different types of antigen-presenting cells affect the induction of experimental autoimmune arthritis. Int Immunol. 1990;2(5):473–476. doi: 10.1093/intimm/2.5.473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Londei M., Savill C. M., Verhoef A., Brennan F., Leech Z. A., Duance V., Maini R. N., Feldmann M. Persistence of collagen type II-specific T-cell clones in the synovial membrane of a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):636–640. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller E. J. Structural studies on cartilage collagen employing limited cleavage and solubilization with pepsin. Biochemistry. 1972 Dec 19;11(26):4903–4909. doi: 10.1021/bi00776a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pals S. T., Radaszkiewicz T., Roozendaal L., Gleichmann E. Chronic progressive polyarthritis and other symptoms of collagen vascular disease induced by graft-vs-host reaction. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1475–1482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plater-Zyberk C., Clarke M. F., Lam K., Mumford P. A., Room G. R., Maini R. N. In vitro immunoglobulin synthesis by lymphocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. I. Effect of monocyte depletion and demonstration of an increased proportion of lymphocytes forming rosettes with mouse erythrocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Jun;52(3):505–511. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranges G. E., Fortin S., Barger M. T., Sriram S., Cooper S. M. In vivo modulation of murine collagen induced arthritis. Int Rev Immunol. 1988 Sep;4(1):83–90. doi: 10.3109/08830188809044772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolphi A., Spiess S., Conradt P., Claesson M. H., Reimann J. CD3+ T cells in severe combined immunodeficiency (scid) mice. II. Transplantation of dm2 lymphoid cells into semi-allogeneic scid mice. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Jul;21(7):1591–1600. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolphi A., Spiess S., Conradt P., Claësson M. H., Reimann J. CD3+ T cells in severe combined immune deficiency (scid) mice. I. Transferred purified CD4+ T cells, but not CD8+ T cells are engrafted in the spleen of congenic scid mice. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Feb;21(2):523–533. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seki N., Sudo Y., Yoshioka T., Sugihara S., Fujitsu T., Sakuma S., Ogawa T., Hamaoka T., Senoh H., Fujiwara H. Type II collagen-induced murine arthritis. I. Induction and perpetuation of arthritis require synergy between humoral and cell-mediated immunity. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 1;140(5):1477–1484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart J. M., Dixon F. J. Serum transfer of collagen-induced arthritis in mice. J Exp Med. 1983 Aug 1;158(2):378–392. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.2.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarkowski A., Klareskog L., Carlsten H., Herberts P., Koopman W. J. Secretion of antibodies to types I and II collagen by synovial tissue cells in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Sep;32(9):1087–1092. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780320906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trentham D. E., Dynesius R. A., David J. R. Passive transfer by cells of type II collagen-induced arthritis in rats. J Clin Invest. 1978 Aug;62(2):359–366. doi: 10.1172/JCI109136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



