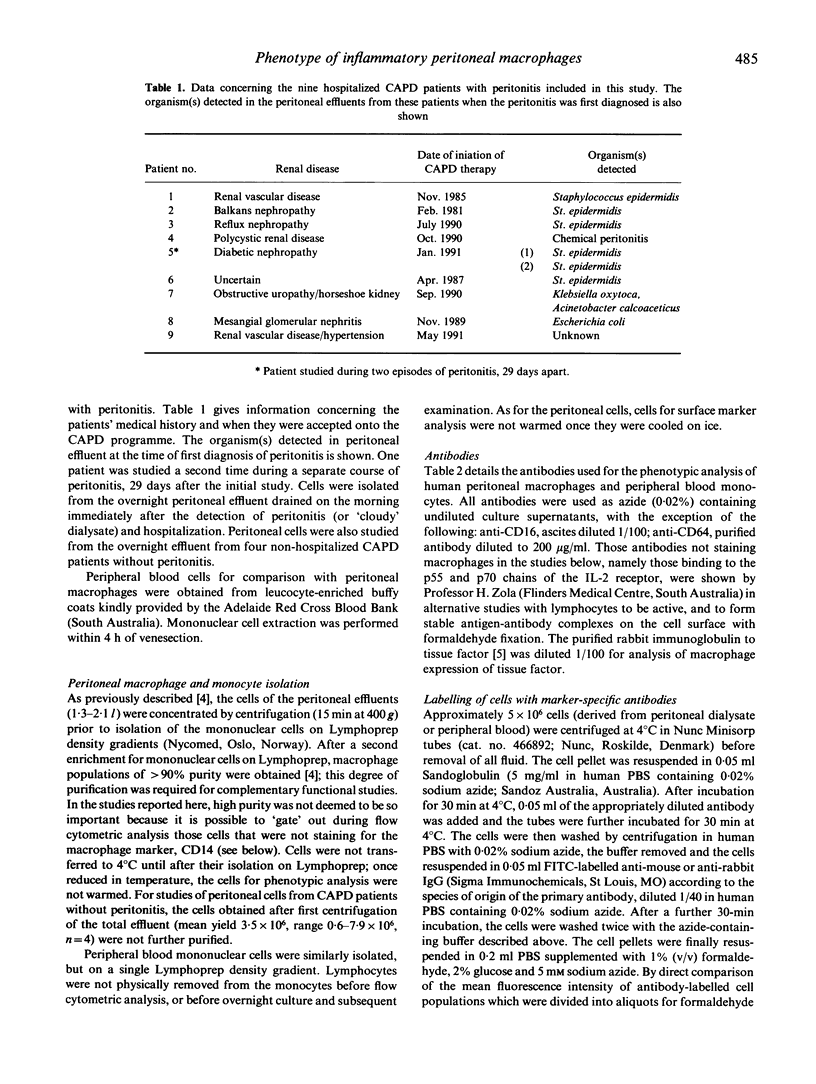
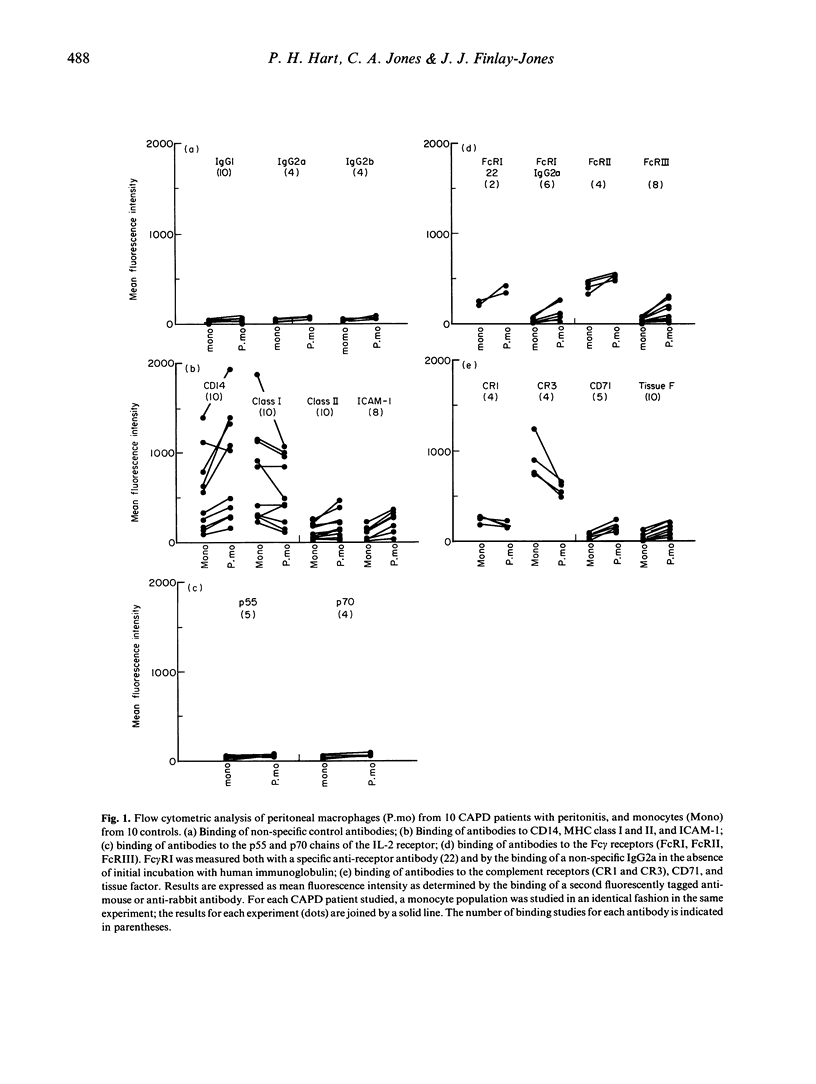
Abstract
The expression of a range of surface molecules/receptors that are important in the host response to infection and foreign antigens was examined using peritoneal macrophages isolated from patients on continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD) with peritonitis. The macrophage phenotypic profile was compared with that of normal peripheral blood monocytes. Consistently there was increased expression by macrophages of CD14, ICAM-1 (CD54), Fc gamma RI (CD64), Fc gamma RII (CDw32), Fc gamma RIII (CD16), transferrin receptors (CD71) and tissue factor. Increased expression of MHC class II was marginally significant. There was no detectable expression of either the p55 (CD25) or p70 chains of the IL-2 receptor. The expression of the complement receptors, CR1 (CD35) and CR3 (CD11b, CD18), was reduced. The activity of well-known inflammatory cytokines, rather than uraemic molecules, can account for the phenotypic profile of these extravasated peritoneal macrophages. The results of this study indicate that peritoneal macrophages from CAPD patients with peritonitis display a phenotype consistent with them being in vivo-derived inflammatory macrophages, and that they are appropriate for use in studies of anti-inflammatory agents.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alobaidi H. M., Coles G. A., Davies M., Lloyd D. Host defence in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis: the effect of the dialysate on phagocyte function. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1986;1(1):16–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C. L., Shen L., Eicher D. M., Wewers M. D., Gill J. K. Phagocytosis mediated by three distinct Fc gamma receptor classes on human leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1990 Apr 1;171(4):1333–1345. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.4.1333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker S., Daniel E. G. Antagonistic and additive effects of IL-4 and interferon-gamma on human monocytes and macrophages: effects on Fc receptors, HLA-D antigens, and superoxide production. Cell Immunol. 1990 Sep;129(2):351–362. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(90)90211-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckman I. G., Bradley J., Brooks D., Zola H. Delineation of serologically distinct monomorphic determinants of human MHC class II antigens: evidence of heterogeneity in their topographical distribution. Mol Immunol. 1984 Mar;21(3):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(84)90075-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckman I., Dimopoulos K., Xu X. N., Ahern M., Bradley J. Age-related changes in the activation requirements of human CD4+ T-cell subsets. Cell Immunol. 1991 Jan;132(1):17–25. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(91)90003-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard D. K., Djeu J. Y. Differential modulation of surface antigens on human macrophages by IFN-gamma and GM-CSF: effect on susceptibility to LAK lysis. J Leukoc Biol. 1991 Jul;50(1):28–34. doi: 10.1002/jlb.50.1.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd A. W., Wawryk S. O., Burns G. F., Fecondo J. V. Intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) has a central role in cell-cell contact-mediated immune mechanisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3095–3099. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. J. Complement receptors and phagocytosis. Curr Opin Immunol. 1991 Feb;3(1):76–82. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(91)90081-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckle A. M., Jayaram Y., Hogg N. Colony-stimulating factors and interferon-gamma differentially affect cell surface molecules shared by monocytes and neutrophils. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Aug;81(2):339–345. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb03342.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erb P., Feldmann M. The role of macrophages in the generation of T-helper cells. II. The genetic control of the macrophage-T-cell interaction for helper cell induction with soluble antigens. J Exp Med. 1975 Aug 1;142(2):460–472. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.2.460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espinoza-Delgado I., Ortaldo J. R., Winkler-Pickett R., Sugamura K., Varesio L., Longo D. L. Expression and role of p75 interleukin 2 receptor on human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1990 May 1;171(5):1821–1826. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.5.1821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanger M. W., Shen L., Graziano R. F., Guyre P. M. Cytotoxicity mediated by human Fc receptors for IgG. Immunol Today. 1989 Mar;10(3):92–99. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90234-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock W. W., Zola H., Atkins R. C. Antigenic heterogeneity of human mononuclear phagocytes: immunohistologic analysis using monoclonal antibodies. Blood. 1983 Dec;62(6):1271–1279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart P. H., Cooper R. L., Finlay-Jones J. J. IL-4 suppresses IL-1 beta, TNF-alpha and PGE2 production by human peritoneal macrophages. Immunology. 1991 Mar;72(3):344–349. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart P. H., Vitti G. F., Burgess D. R., Whitty G. A., Piccoli D. S., Hamilton J. A. Potential antiinflammatory effects of interleukin 4: suppression of human monocyte tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin 1, and prostaglandin E2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3803–3807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg N., Ross G. D., Jones D. B., Slusarenko M., Walport M. J., Lachmann P. J. Identification of an anti-monocyte monoclonal antibody that is specific for membrane complement receptor type one (CR1). Eur J Immunol. 1984 Mar;14(3):236–243. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paborsky L. R., Fendly B. M., Fisher K. L., Lawn R. M., Marks B. J., McCray G., Tate K. M., Vehar G. A., Gorman C. M. Mammalian cell transient expression of tissue factor for the production of antigen. Protein Eng. 1990 May;3(6):547–553. doi: 10.1093/protein/3.6.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranscht B., Clapshaw P. A., Price J., Noble M., Seifert W. Development of oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells studied with a monoclonal antibody against galactocerebroside. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2709–2713. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan J., Geczy C. L. Characterization and purification of mouse macrophage procoagulant-inducing factor. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 1;137(9):2864–2870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan J., Geczy C. Coagulation and the expression of cell-mediated immunity. Immunol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;65(Pt 2):127–139. doi: 10.1038/icb.1987.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabo G., Miller-Graziano C. L. Induction and regulation of monocyte procoagulant activity. Transplantation. 1990 Aug;50(2):301–309. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199008000-00026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemura R., Werb Z. Secretory products of macrophages and their physiological functions. Am J Physiol. 1984 Jan;246(1 Pt 1):C1–C9. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1984.246.1.C1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi A. K., Taplits M., Puri J., Hoffman T. Down-regulation of surface FcRI and decrease in antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity of cultured monocytes. Reversal by monensin or cytochalasin-D. J Immunol. 1991 Feb 15;146(4):1309–1315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsudo M., Karasuyama H., Kitamura F., Tanaka T., Kubo S., Yamamura Y., Tamatani T., Hatakeyama M., Taniguchi T., Miyasaka M. The IL-2 receptor beta-chain (p70). Ligand binding ability of the cDNA-encoding membrane and secreted forms. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 15;145(2):599–606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C., Scigliano E., Freedman V. H. Structure and function of human and murine receptors for IgG. Annu Rev Immunol. 1988;6:251–281. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.06.040188.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Seventer G. A., Shimizu Y., Horgan K. J., Shaw S. The LFA-1 ligand ICAM-1 provides an important costimulatory signal for T cell receptor-mediated activation of resting T cells. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 15;144(12):4579–4586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf H. M., Mannhalter J. W., Salzmann H. C., Göttlicher J., Ahmad R., Eibl M. M. Phagocytosis of serum-opsonized zymosan down-regulates the expression of CR3 and FcRI in the membrane of human monocytes. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 15;141(10):3537–3543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Ramos R. A., Tobias P. S., Ulevitch R. J., Mathison J. C. CD14, a receptor for complexes of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and LPS binding protein. Science. 1990 Sep 21;249(4975):1431–1433. doi: 10.1126/science.1698311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zola H., Macardle P. J., Flego L., Webster J. The expression of sub-population markers on B cells: a re-evaluation using high-sensitivity fluorescence flow cytometry. Dis Markers. 1991 Mar-Apr;9(2):103–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zola H., Moore H. A., Hunter I. K., Bradley J. Analysis of chemical and biochemical properties of membrane molecules in situ by analytical flow cytometry with monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Nov 16;74(1):65–77. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90368-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- te Velde A. A., Klomp J. P., Yard B. A., de Vries J. E., Figdor C. G. Modulation of phenotypic and functional properties of human peripheral blood monocytes by IL-4. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 1;140(5):1548–1554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


