Abstract
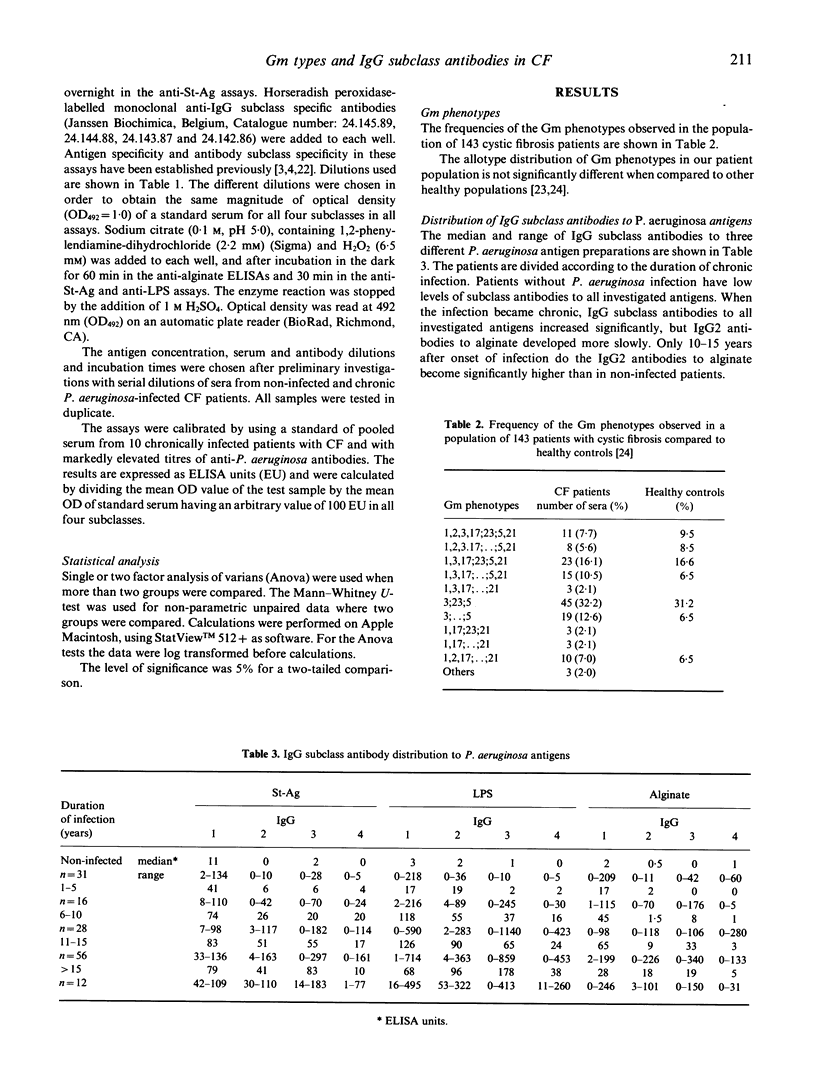
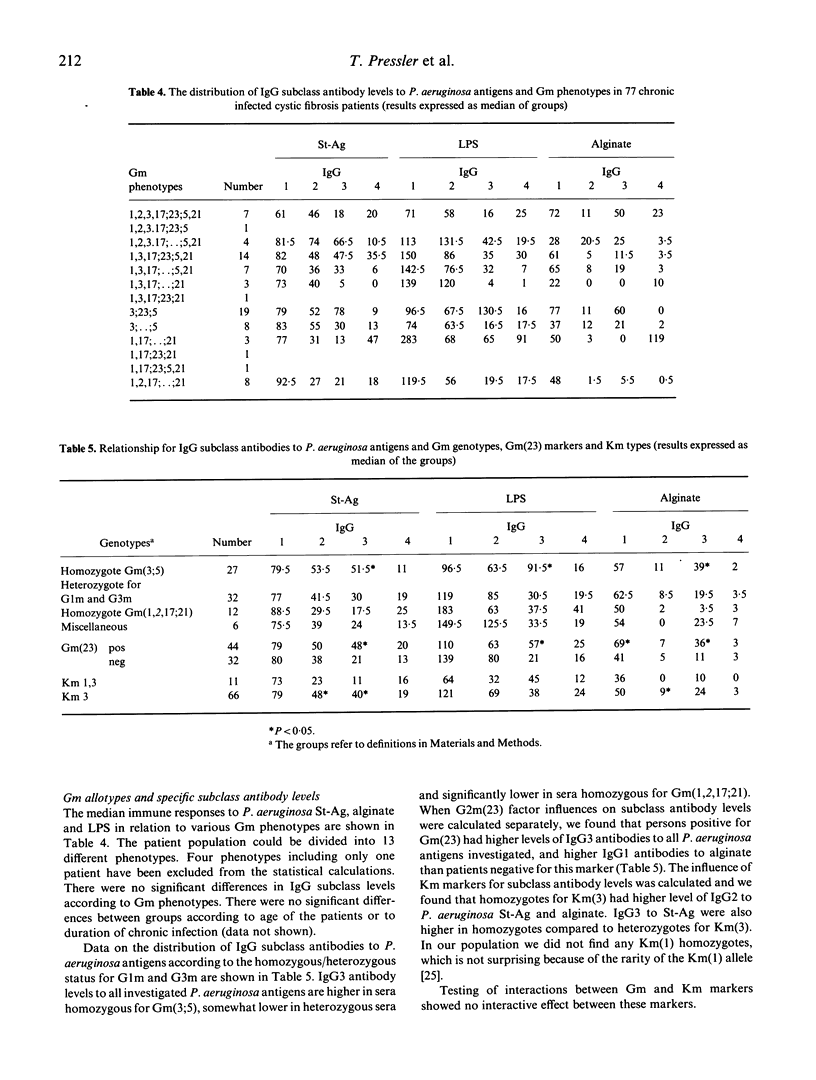
Chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infection is the leading cause of death in patients with cystic fibrosis (CF). Poor prognosis correlates with a high number of anti-pseudomonas precipitins and with high levels of IgG2 and IgG3 anti-pseudomonas antibodies. Reports of several highly significant associations between certain Gm (genetic markers of IgG on human chromosome 14) and Km (k-type light chain determinants on chromosome 2) phenotypes and immune responsiveness to various antigens suggest that allotype-linked immune response genes do exist in man. Furthermore correlation between Gm types and IgG subclass levels has been reported. A group of 143 CF patients were investigated (31 non-infected and 112 chronic infected). The IgG subclass antibodies to three different P. aeruginosa antigens (P. aeruginosa standard antigen (St-Ag), alginate and LPS) were determined. Immunoglobulin allotypes were determined by haemagglutination inhibition. Samples were typed for G1m(1,2,3, and 17), G2m(23), G3m(5,21), and Km(1,3). Statistical analysis of our data demonstrate that IgG3 anti-pseudomonas antibody levels and Gm markers are related. IgG3 antibody levels to all investigated P. aeruginosa antigens are significantly higher in sera homozygous for Gm(3;5), somewhat lower in heterozygous sera, and significantly lower in sera homozygous for Gm(1,2,17;21). We suggest that genetic differences between the patients may explain the present differences in subclass patterns.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander M. D., Andrews J. A., Leslie R. G., Wood N. J. The binding of human and guinea-pig IgG subclasses to homologous macrophage and monocyte Fc receptors. Immunology. 1978 Jul;35(1):115–123. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corey M., Levison H., Crozier D. Five- to seven-year course of pulmonary function in cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Dec;114(6):1085–1092. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.114.6.1085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fick R. B., Jr, Olchowski J., Squier S. U., Merrill W. W., Reynolds H. Y. Immunoglobulin-G subclasses in cystic fibrosis. IgG2 response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa lipopolysaccharide. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Mar;133(3):418–422. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.133.3.418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fomsgaard A., Conrad R. S., Galanos C., Shand G. H., Høiby N. Comparative immunochemistry of lipopolysaccharides from typable and polyagglutinable Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from patients with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 May;26(5):821–826. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.5.821-826.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fomsgaard A., Dinesen B., Shand G. H., Pressler T., Høiby N. Antilipopolysaccharide antibodies and differential diagnosis of chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infection in cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jun;27(6):1222–1229. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.6.1222-1229.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granoff D. M., Pandey J. P., Boies E., Squires J., Munson R. S., Jr, Suarez B. Response to immunization with Haemophilus influenzae type b polysaccharide-pertussis vaccine and risk of Haemophilus meningitis in children with the Km(1) immunoglobulin allotype. J Clin Invest. 1984 Nov;74(5):1708–1714. doi: 10.1172/JCI111588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granoff D. M., Sheetz K., Pandey J. P., Nahm M. H., Rambeck J. H., Jacobs J. L., Musser J., Selander R. K., Kabeer M., Murphy T. V. Host and bacterial factors associated with Haemophilus influenzae type b disease in Minnesota children vaccinated with type b polysaccharide vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1989 May;159(5):908–916. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.5.908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubb R., Hallberg T., Hammarström L., Oxelius V. A., Smith C. I., Söderström R., Söderström T. Correlation between deficiency of immunoglobulin subclass G3 and Gm allotype. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand C. 1986 Oct;94(5):187–191. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1986.tb02110.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassan M. S., Islam K. B., Hammarström L., Smith C. I. Regulation of C gamma 3 expression. Role of switch in the allotype-associated variation of human serum IgG3 levels. J Immunol. 1992 Apr 15;148(8):2555–2562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Høiby N., Döring G., Schiøtz P. O. The role of immune complexes in the pathogenesis of bacterial infections. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1986;40:29–53. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.000333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Høiby N., Koch C. Cystic fibrosis. 1. Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in cystic fibrosis and its management. Thorax. 1990 Nov;45(11):881–884. doi: 10.1136/thx.45.11.881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferis R., Reimer C. B., Skvaril F., de Lange G., Ling N. R., Lowe J., Walker M. R., Phillips D. J., Aloisio C. H., Wells T. W. Evaluation of monoclonal antibodies having specificity for human IgG sub-classes: results of an IUIS/WHO collaborative study. Immunol Lett. 1985;10(3-4):223–252. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(85)90082-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen H. K., Nir M., Høiby N., Koch C., Schwartz M. Severity of cystic fibrosis in patients homozygous and heterozygous for delta F508 mutation. Lancet. 1991 Mar 16;337(8742):631–634. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92449-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagnoff M. F. Two genetic loci control the murine immune response to A-gliadin, a wheat protein that activates coeliac sprue. Nature. 1982 Mar 11;296(5853):158–160. doi: 10.1038/296158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell A., Skvaril F., Steinberg A. G., Van Loghem E., Terry W. D. Correlations between the concentrations of the four sub-classes of IgG and Gm Allotypes in normal human sera. J Immunol. 1972 Jan;108(1):195–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell A., Vassalli G., DeLange G. G., Skvaril F., Ambrosino D. M., Siber G. R. Ig allotype-linked regulation of class and subclass composition of natural antibodies to group A streptococcal carbohydrate. J Immunol. 1989 Apr 1;142(7):2495–2500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow P. R., Rennick D. M., Benjamini E. The antibody response to a single antigenic determinant of the tobacco mosaic virus protein (TMVP): effects of allotype-linked genes and restricted heterogeneity of the response. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2875–2881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss R. B., Hsu Y. P., Van Eede P. H., Van Leeuwen A. M., Lewiston N. J., De Lange G. Altered antibody isotype in cystic fibrosis: impaired natural antibody response to polysaccharide antigens. Pediatr Res. 1987 Dec;22(6):708–713. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198712000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima I., Isobe K., Yoshida T., Iwamoto T., Nagase F., Zhang Y. H., Pu M., Lwin T. Allotype-linked immune response genes: roles in network control of the immune system. Exp Clin Immunogenet. 1991;8(3):121–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojeniyi B., Høiby N., Rosdahl V. T. Prevalence and persistence of polyagglutinable Pseudomonas aeruginosa in isolates from cystic fibrosis patients. APMIS. 1991 Feb;99(2):187–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandey J. P., Baker C. J., Kasper D. L., Fudenberg H. H. Two unlinked genetic loci interact to control the human immune response to type III group B streptococcal antigen. J Immunogenet. 1984 Apr;11(2):159–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-313x.1984.tb01051.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen S. S., Espersen F., Høiby N., Shand G. H. Purification, characterization, and immunological cross-reactivity of alginates produced by mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa from patients with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Apr;27(4):691–699. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.4.691-699.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perelmutter L. IgG4 and the immune system. Clin Rev Allergy. 1983 Jun;1(2):267–287. doi: 10.1007/BF02991162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pressler T., Mansa B., Jensen T., Pedersen S. S., Høiby N., Koch C. Increased IgG2 and IgG3 concentration is associated with advanced Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection and poor pulmonary function in cystic fibrosis. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1988 Jul;77(4):576–582. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1988.tb10703.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pressler T., Pedersen S. S., Espersen F., Høiby N., Koch C. IgG subclass antibodies to Pseudomonas aeruginosa in sera from patients with chronic Ps. aeruginosa infection investigated by ELISA. Clin Exp Immunol. 1990 Sep;81(3):428–434. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1990.tb05351.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pressler T., Pedersen S. S., Espersen F., Høiby N., Koch C. IgG subclass antibody responses to alginate from Pseudomonas aeruginosa in patients with cystic fibrosis and chronic P. aeruginosa infection. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1992 Sep;14(1):44–51. doi: 10.1002/ppul.1950140109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarvas H., Rautonen N., Mäkelä O. Allotype-associated differences in concentrations of human IgG subclasses. J Clin Immunol. 1991 Jan;11(1):39–45. doi: 10.1007/BF00918793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumaker V. N., Calcott M. A., Spiegelberg H. L., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Ultracentifuge studies of the binding of IgG of different subclasses to the Clq subunit of the first component of complement. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 16;15(23):5175–5181. doi: 10.1021/bi00668a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shryock T. R., Mollé J. S., Klinger J. D., Thomassen M. J. Association with phagocytic inhibition of anti-Pseudomonas aeruginosa immunoglobulin G antibody subclass levels in serum from patients with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Mar;23(3):513–516. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.3.513-516.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittingham S., Mathews J. D., Schanfield M. S., Matthews J. V., Tait B. D., Morris P. J., Mackay I. R. Interactive effect of Gm allotypes and HLA-B locus antigens on the human antibody response to a bacterial antigen. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Apr;40(1):8–15. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wine J. J. Cystic fibrosis. The mutant protein responds. Nature. 1991 Dec 19;354(6354):503–504. doi: 10.1038/354503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yount W. J., Kunkel H. G., Litwin S. D. Studies of the Vi (gamma-2c) subgroup of gamma-globulin. A relationship between concentration and genetic type among normal individuals. J Exp Med. 1967 Jan 1;125(1):177–190. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.1.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


