FIG. 3.
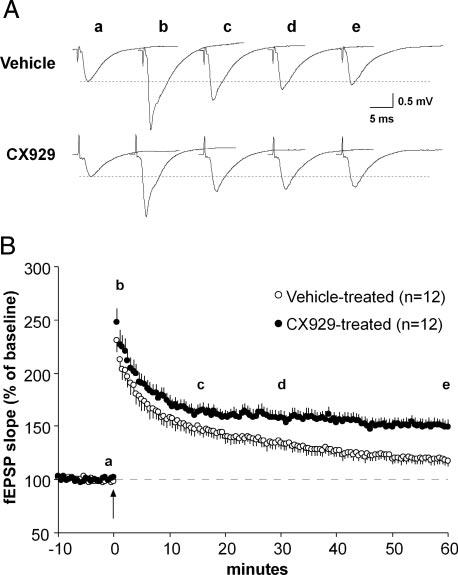
Ampakine pretreatment rescues long-term potentiation (LTP) stabilization in middle-aged rats. Basal dendritic fEPSPs (elicited by stimulation of the Schaffer collateral/commissural afferents to CA1b SO as illustrated in Fig. 1B) were compared for slices from middle-aged rats that received CX929 or vehicle injections for 4 days. Slices were prepared 18 h after the last injections. A: representative fEPSP traces (a-e) collected during the baseline period and 1, 15, 30, and 60 min (from left to right) after theta-burst stimulation from vehicle- and CX929-treated rats. Figures are averages of 3 consecutive traces. B: plot of group mean (±SE) fEPSP slopes recorded in slices from ampakine-treated (filled circle) and vehicle-treated (open circle) rats. Theta bursts were delivered (time 0, arrow) after establishing that baseline responses (3/min) were constant over 10-20 min. Letters a-e indicate the time points for traces shown in A. As shown, slices from ampakine- and vehicle-treated rats had approximately equal degrees of potentiation immediately after TBS. Responses in slices from CX929-treated rats settled to a stable level by 20 min post-TBS and persisted there through 60 min of testing. In contrast, responses in slices from vehicle-treated rats steadily declined toward baseline values from the initial peak: percentage potentiation at 60 min post-TBS was significantly greater in the ampakine-treatment group than in controls (P < 0.001 for minutes 50-60 post-TBS).
