Abstract
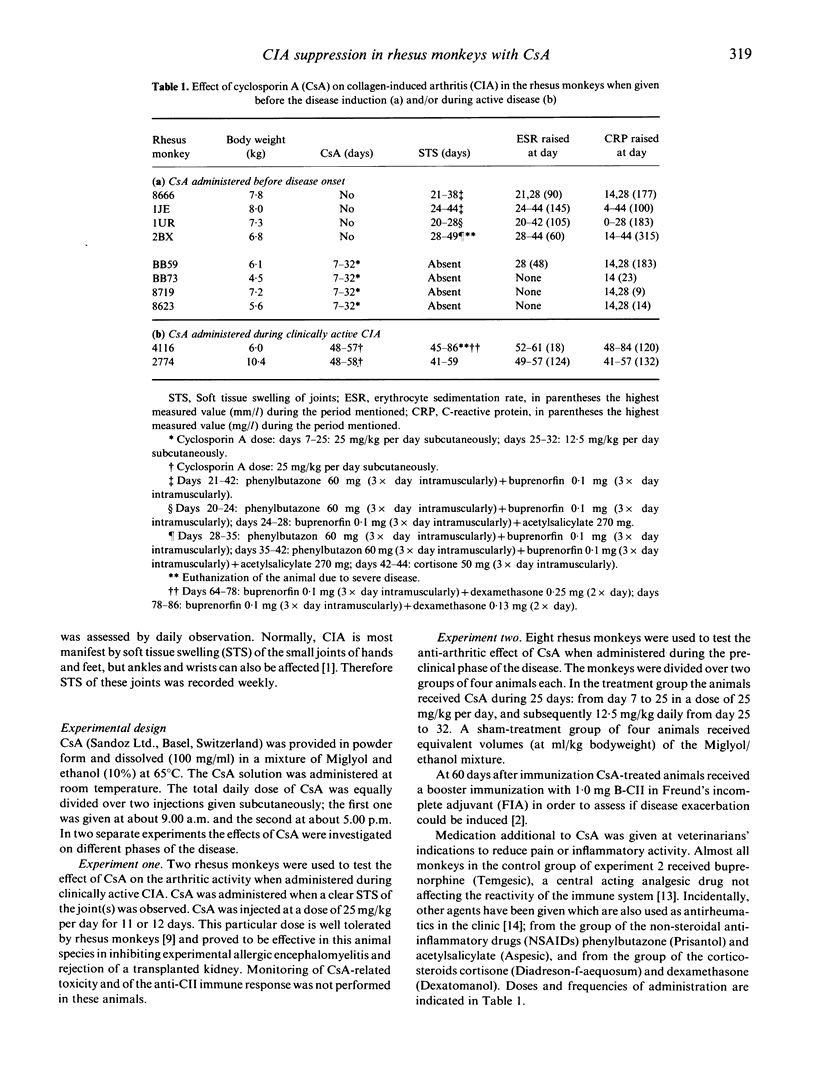
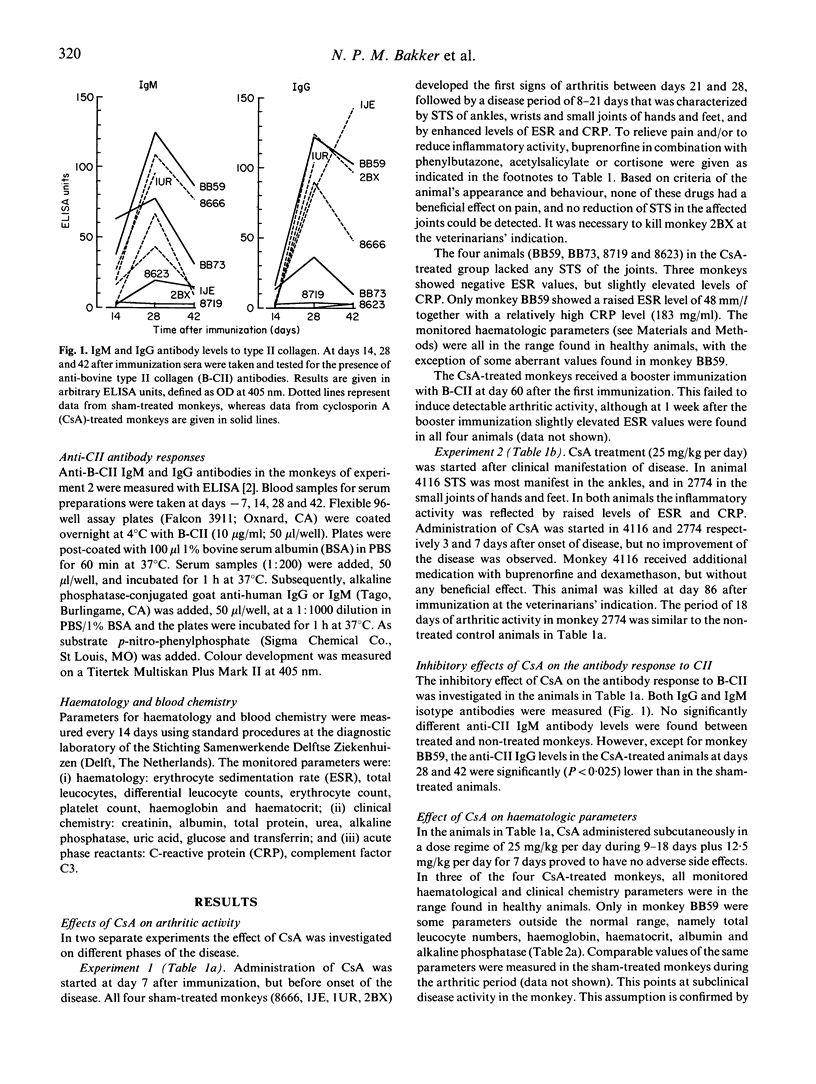
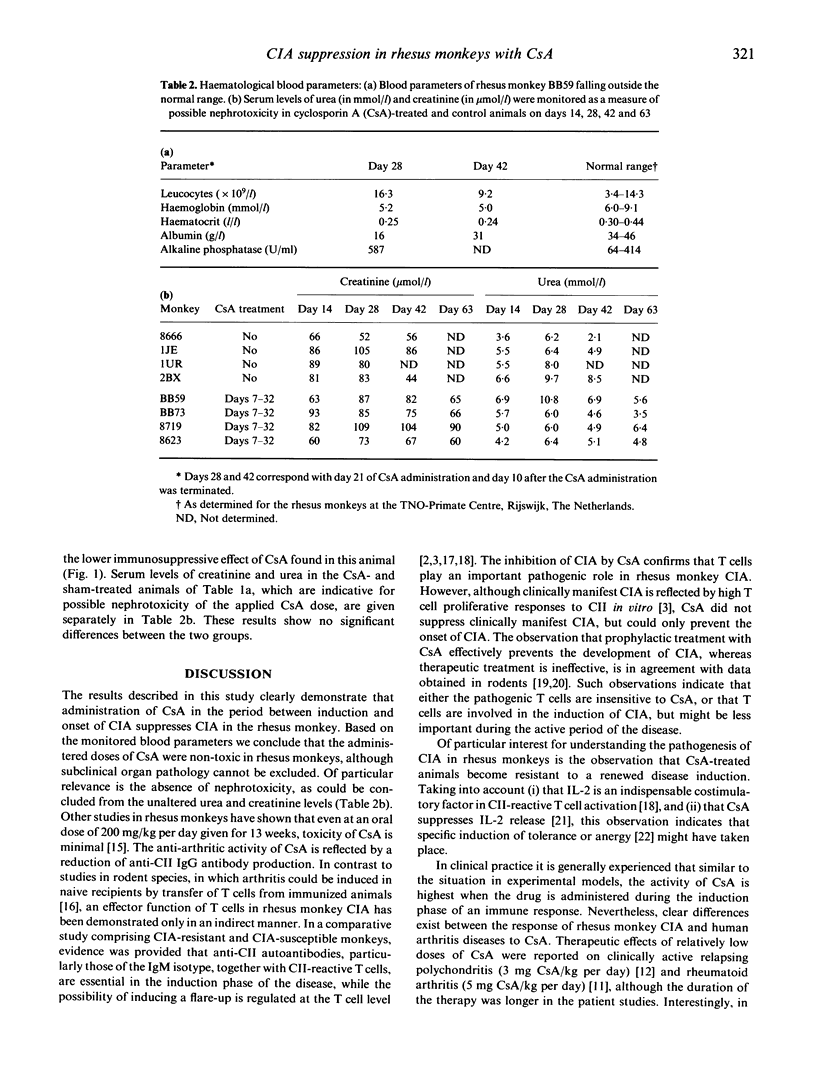
The influence of cyclosporin A (CsA) on type II collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) in the rhesus monkey has been investigated. CsA was administered subcutaneously in a dose of 25 mg/kg per day during 9-18 days and additionally 12.5 mg/kg per day for 7 days. At this dosing regime no significant alterations of haematologic parameters were found, indicating that the toxicity of CsA was negligible. Administration of CsA after onset of arthritis had no beneficial effect, but when given between immunization and manifestation of clinical symptoms, CIA could be prevented completely. Moreover, these monkeys became resistant to the disease, because no arthritic activity could be observed upon a booster immunization with type II collagen (CII). The suppression of disease by CsA is reflected in reduced antibody levels to CII.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anstey A., Mayou S., Morgan K., Clague R. B., Munro D. D. Relapsing polychondritis: autoimmunity to type II collagen and treatment with cyclosporin A. Br J Dermatol. 1991 Dec;125(6):588–591. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1991.tb14801.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker N. P., van Erck M. G., 't Hart L. A., Jonker M. Acquired resistance to type II collagen-induced arthritis in rhesus monkeys is reflected by a T cell low-responsiveness to the antigen. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Nov;86(2):219–223. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05799.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker N. P., van Erck M. G., Botman C. A., Jonker M., 't Hart B. A. Collagen-induced arthritis in an outbred group of rhesus monkeys comprising responder and nonresponder animals. Relationship between the course of arthritis and collagen-specific immunity. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 May;34(5):616–624. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker N. P., van Erck M. G., Otting N., Lardy N. M., Noort R. C., 't Hart B. A., Jonker M., Bontrop R. E. Resistance to collagen-induced arthritis in a nonhuman primate species maps to the major histocompatibility complex class I region. J Exp Med. 1992 Apr 1;175(4):933–937. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.4.933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker N. P., van Erck M. G., Zurcher C., Faaber P., Lemmens A., Hazenberg M., Bontrop R. E., Jonker M. Experimental immune mediated arthritis in rhesus monkeys. A model for human rheumatoid arthritis? Rheumatol Int. 1990;10(1):21–29. doi: 10.1007/BF02274777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borel J. F. Comparative study of in vitro and in vivo drug effects on cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Immunology. 1976 Oct;31(4):631–641. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunjes D., Hardt C., Röllinghoff M., Wagner H. Cyclosporin A mediates immunosuppression of primary cytotoxic T cell responses by impairing the release of interleukin 1 and interleukin 2. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Aug;11(8):657–661. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830110812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cacalano N. A., Chen B. X., Cleveland W. L., Erlanger B. F. Evidence for a functional receptor for cyclosporin A on the surface of lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4353–4357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Essery G., Feldmann M., Lamb J. R. Interleukin-2 can prevent and reverse antigen-induced unresponsiveness in cloned human T lymphocytes. Immunology. 1988 Jul;64(3):413–417. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart B. A., Bakker N. P., Jonker M., Bontrop R. E. Resistance to collagen-induced arthritis in rats and rhesus monkeys after immunization with attenuated type II collagen. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Jul;23(7):1588–1594. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heel R. C., Brogden R. N., Speight T. M., Avery G. S. Buprenorphine: a review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic efficacy. Drugs. 1979 Feb;17(2):81–110. doi: 10.2165/00003495-197917020-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson B., Staines N. A., Burrai I., Cox J. H. The anti-arthritic and immunosuppressive effects of cyclosporine on arthritis induced in the rat by type II collagen. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Jul;57(1):51–56. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaibara N., Hotokebuchi T., Takagishi K., Katsuki I. Paradoxical effects of cyclosporin A on collagen arthritis in rats. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):2007–2015. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krönke M., Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Arya S. K., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C., Waldmann T. A., Greene W. C. Cyclosporin A inhibits T-cell growth factor gene expression at the level of mRNA transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5214–5218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryffel B., Donatsch P., Madörin M., Matter B. E., Rüttimann G., Schön H., Stoll R., Wilson J. Toxicological evaluation of cyclosporin A. Arch Toxicol. 1983 Jun;53(2):107–141. doi: 10.1007/BF00302721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seki N., Sudo Y., Yoshioka T., Sugihara S., Fujitsu T., Sakuma S., Ogawa T., Hamaoka T., Senoh H., Fujiwara H. Type II collagen-induced murine arthritis. I. Induction and perpetuation of arthritis require synergy between humoral and cell-mediated immunity. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 1;140(5):1477–1484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens H. P., Hovius S. E., Heeney J. L., van Nierop P. W., Jonker M. Immunologic aspects and complications of composite tissue allografting for upper extremity reconstruction: a study in the rhesus monkey. Transplant Proc. 1991 Feb;23(1 Pt 1):623–625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiller C. R., Dupré J., Gent M., Jenner M. R., Keown P. A., Laupacis A., Martell R., Rodger N. W., von Graffenried B., Wolfe B. M. Effects of cyclosporine immunosuppression in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus of recent onset. Science. 1984 Mar 30;223(4643):1362–1367. doi: 10.1126/science.6367043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


