Abstract
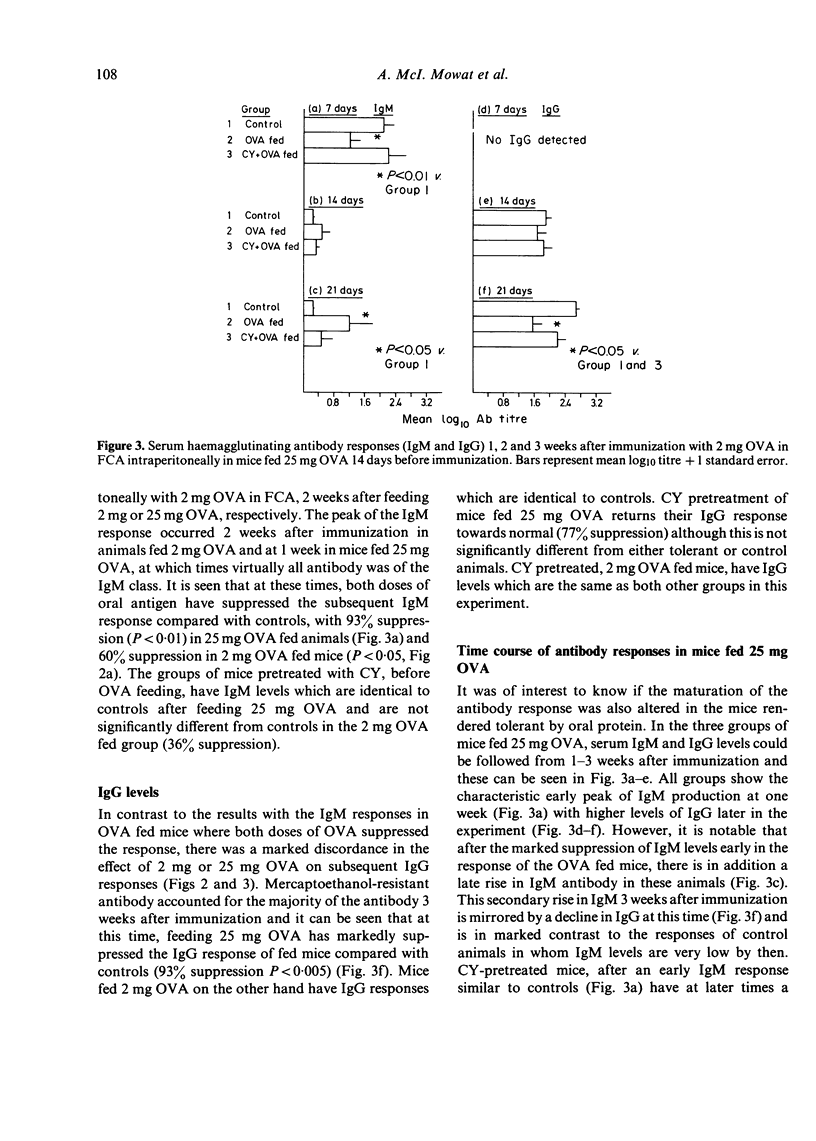
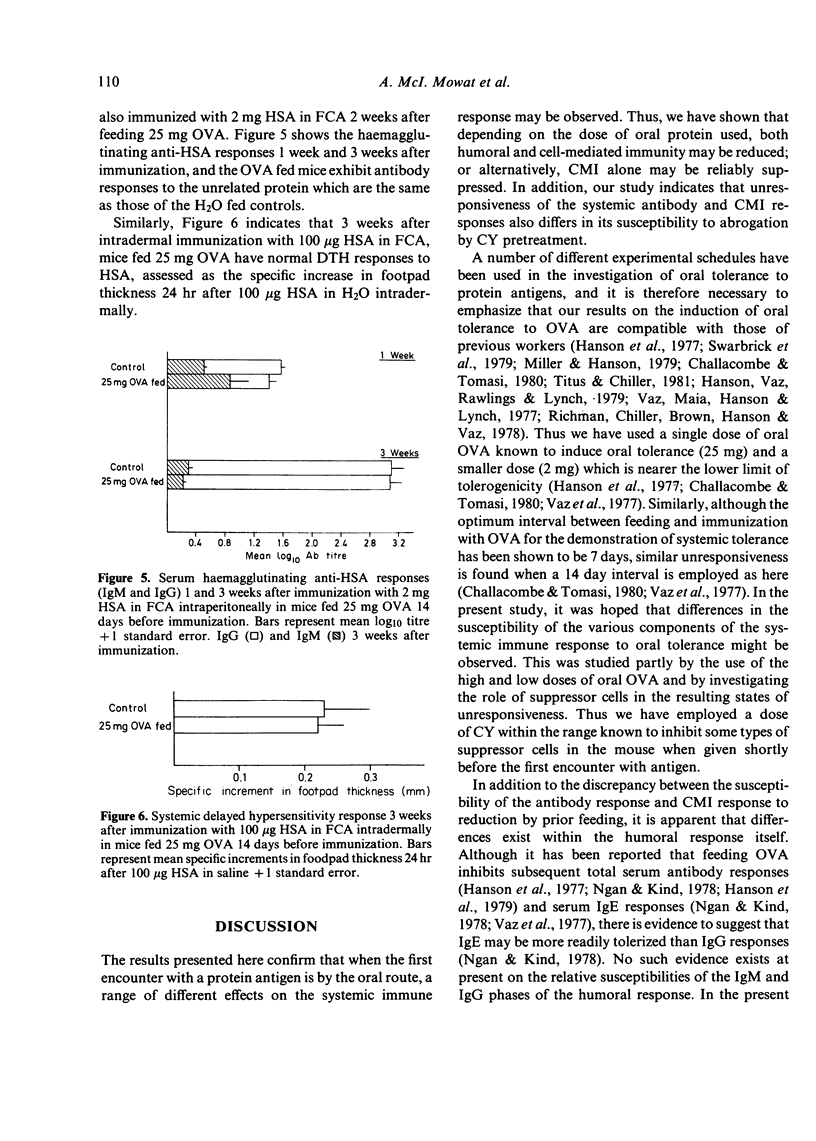
Feeding ovalbumin over a wide range of doses is known to reduce subsequent systemic immune responses to parenteral immunization. In the present study, we have fed mice 2 mg and 25 mg ovalbumin (OVA) 2 weeks before systemic immunization and followed the resulting humoral antibody and cell-mediated immune (CMI) responses. The results indicate that while 25 mg OVA will reduce subsequent IgM, IgG and CMI responses to OVA, feeding 2 mg OVA will only suppress CMI responses and to a lesser extent the IgM response. Furthermore, the tolerant state induced by feeding 25 mg OVA was only partially prevented by 100 mg/kg cyclophosphamide (CY) while the suppressed CMI after feeding 2 mg OVA was completely blocked by CY pretreatment. These findings suggest that the humoral and cell-mediated limbs of the immune response may be controlled by different regulatory systems after feeding antigen, and that activation of these systems is dependent on the dose of oral antigen use. In addition, the results are in agreement with our previous finding that CY pretreatment will allow the development of CMI in the gut and gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT) after oral OVA and suggest that this phenomenon is related to breakdown of oral tolerance induction.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- André C., Heremans J. F., Vaerman J. P., Cambiaso C. L. A mechanism for the induction of immunological tolerance by antigen feeding: antigen-antibody complexes. J Exp Med. 1975 Dec 1;142(6):1509–1519. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.6.1509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asherson G. L., Zembala M., Perera M. A., Mayhew B., Thomas W. R. Production of immunity and unresponsiveness in the mouse by feeding contact sensitizing agents and the role of suppressor cells in the peyer's patches, mesenteric lymph nodes and other lymphoid tissues. Cell Immunol. 1977 Sep;33(1):145–155. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90142-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Askenase P. W., Hayden B. J., Gershon R. K. Augmentation of delayed-type hypersensitivity by doses of cyclophosphamide which do not affect antibody responses. J Exp Med. 1975 Mar 1;141(3):697–702. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.3.697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basten A., Miller J. F., Sprent J., Cheers C. Cell-to-cell interaction in the immune response. X. T-cell-dependent suppression in tolerant mice. J Exp Med. 1974 Jul 1;140(1):199–217. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.1.199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challacombe S. J., Tomasi T. B., Jr Systemic tolerance and secretory immunity after oral immunization. J Exp Med. 1980 Dec 1;152(6):1459–1472. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.6.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabbé P. A., Nash D. R., Bazin H., Eyssen D. V., Heremans J. F. Antibodies of the IgA type in intestinal plasma cells of germfree mice after oral or parenteral immunization with ferritin. J Exp Med. 1969 Oct 1;130(4):723–744. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.4.723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ecknauer R., Löhrs U. The effect of a single dose of cyclophosphamide on the jejunum of specified pathogenfree and germfree rats. Digestion. 1976;14(3):269–280. doi: 10.1159/000197940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endres R. O., Grey H. M. Antigen recognition by T cells. II. Intravenous administration of native or denatured ovalbumin results in tolerance to both forms of the antigen. J Immunol. 1980 Oct;125(4):1521–1525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill H. K., Liew F. Y. Regulation of delayed-type hypersensitivity. III. Effect of cyclophosphamide on the suppressor cells for delayed-type hypersensitivity to sheep erythrocytes in mice. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Mar;8(3):172–176. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson D. G., Vaz N. M., Maia L. C., Hornbrook M. M., Lynch J. M., Roy C. A. Inhibition of specific immune responses by feeding protein antigens. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1977;55(1-6):526–532. doi: 10.1159/000231966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson D. G., Vaz N. M., Rawlings L. A., Lynch J. M. Inhibition of specific immune responses by feeding protein antigens. II. Effects of prior passive and active immunization. J Immunol. 1979 Jun;122(6):2261–2266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwich G., Weisshaar K., Domschke W. Intestinale Disaccharidasen der Ratte under Cyclophosphamid-Behandlung. Arzneimittelforschung. 1978;28(6):973–976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagnoff M. F. Effects of antigen-feeding on intestinal and systemic immune responses. II. Suppression of delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions. J Immunol. 1978 May;120(5):1509–1513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagnoff M. F. Effects of antigen-feeding on intestinal and systemic immune responses. III. Antigen-specific serum-mediated suppression of humoral antibody responses after antigen feeding. Cell Immunol. 1978 Sep 15;40(1):186–203. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90326-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattingly J. A., Waksman B. H. Immunologic suppression after oral administration of antigen. I. Specific suppressor cells formed in rat Peyer's patches after oral administration of sheep erythrocytes and their systemic migration. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):1878–1883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattingly J. A., Waksman B. H. Immunologic suppression after oral administration of antigen. II. Antigen-specific helper and suppressor factors produced by spleen cells of rats fed sheep erythrocytes. J Immunol. 1980 Sep;125(3):1044–1047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. D., Hanson D. G. Inhibition of specific immune responses by feeding protein antigens. IV. Evidence for tolerance and specific active suppression of cell-mediated immune responses to ovalbumin. J Immunol. 1979 Nov;123(5):2344–2350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowat A. M., Ferguson A. Hypersensitivity in the small intestinal mucosa. V. Induction of cell-mediated immunity to a dietary antigen. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Mar;43(3):574–582. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neveu P. J., Borduas A. G. Carrier function in immune deviation. J Immunol. 1974 Mar;112(3):1264–1266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ngan J., Kind L. S. Suppressor T cells for IgE and IgG in Peyer's patches of mice made tolerant by the oral administration of ovalbumin. J Immunol. 1978 Mar;120(3):861–865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks D. E., Weigle W. O. Maintenance of immunologic unresponsiveness to human gamma-globulin: evidence for irreversible inactivation in B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1980 Mar;124(3):1230–1236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polak L., Geleick H., Turk J. L. Reversal by cyclophosphamide of tolerance in contact sensitization. Tolerance induced by prior feeding with DNCB. Immunology. 1975 May;28(5):939–942. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman L. K., Chiller J. M., Brown W. R., Hanson D. G., Vaz N. M. Enterically induced immunologic tolerance. I. Induction of suppressor T lymphoyctes by intragastric administration of soluble proteins. J Immunol. 1978 Dec;121(6):2429–2434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver J., Benacerraf B. Dissociation of T cell helper function and delayed hypersensitivity. J Immunol. 1974 Dec;113(6):1872–1875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swarbrick E. T., Stokes C. R., Soothill J. F. Absorption of antigens after oral immunisation and the simultaneous induction of specific systemic tolerance. Gut. 1979 Feb;20(2):121–125. doi: 10.1136/gut.20.2.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas H. C., Parrott M. V. The induction of tolerance to a soluble protein antigen by oral administration. Immunology. 1974 Oct;27(4):631–639. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titus R. G., Chiller J. M. Orally induced tolerance. Definition at the cellular level. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1981;65(3):323–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaz N. M., Maia L. C., Hanson D. G., Lynch J. M. Inhibition of homocytotropic antibody responses in adult inbred mice by previous feeding of the specific antigen. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1977 Aug;60(2):110–115. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(77)90035-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vives J., Parks D. E., Weigle W. O. Immunologic unresponsiveness after gastric administration of human gamma-globulin: antigen requirements and cellular parameters. J Immunol. 1980 Oct;125(4):1811–1816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


