Abstract
Details are given of a system for keyhole limpet haemocyanin (KLH)-induced DNA synthesis by murine T lymphocytes in vitro. Lymph node T cells from mice primed with KLH and Bordetella pertussis were stimulated with KLH under the defined conditions, and it was found that such cultured cells exhibited substantial non-specific helper activity. In contrast similarly primed T cells which had not been cultured showed only antigen-specific help. It is concluded that proper account should be taken of non-specific effects when studying the activity of antigen-specific helper cells in in vitro.
Full text
PDF

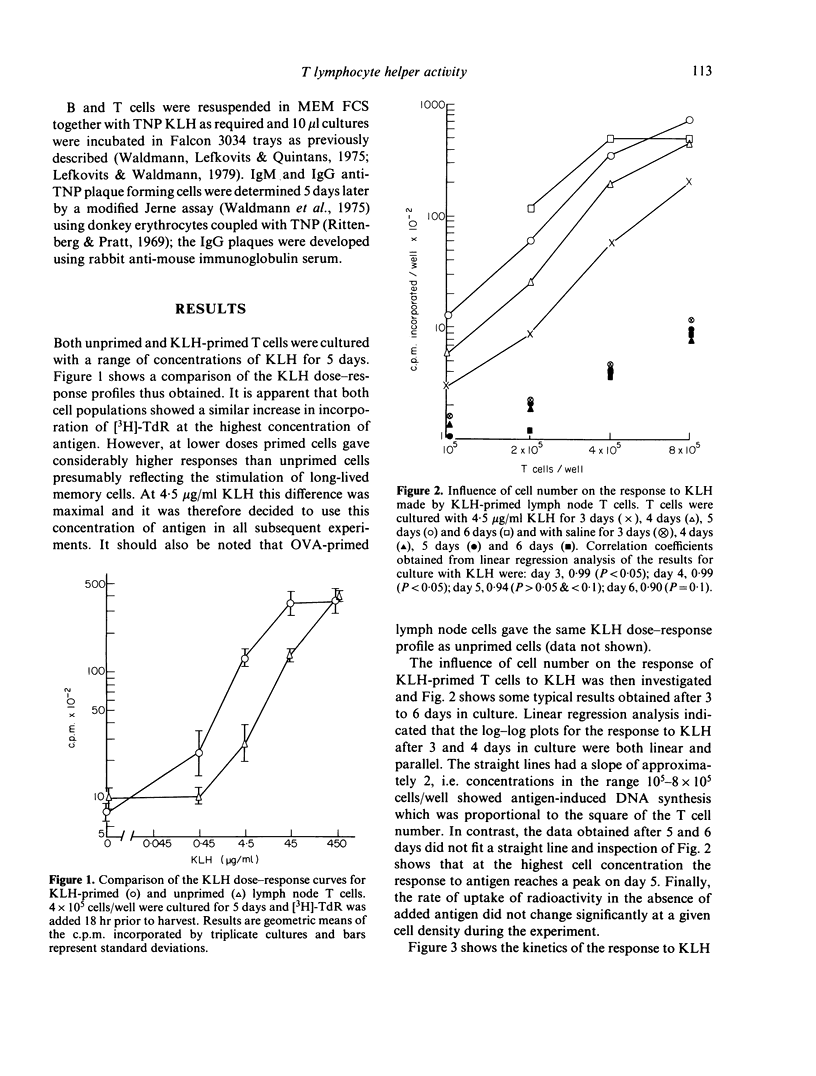
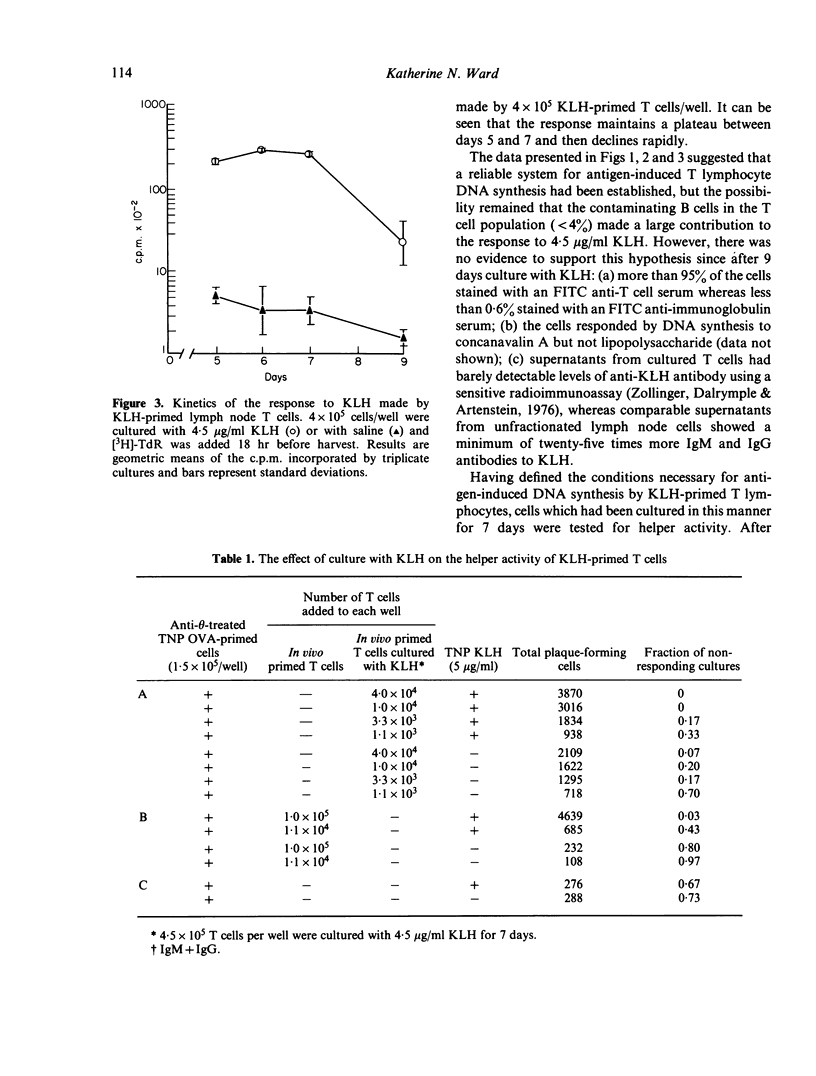


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyle W. An extension of the 51Cr-release assay for the estimation of mouse cytotoxins. Transplantation. 1968 Sep;6(6):761–764. doi: 10.1097/00007890-196809000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor H., Asofsky R. Synergy among lymphoid cells mediating the graft-versus-host response. 3. Evidence for interaction between two types of thymus-derived cells. J Exp Med. 1972 Apr 1;135(4):764–779. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.4.764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Click R. E., Benck L., Alter B. J. Immune responses in vitro. I. Culture conditions for antibody synthesis. Cell Immunol. 1972 Feb;3(2):264–276. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90165-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corradin G., Etlinger H. M., Chiller J. M. Lymphocyte specificity to protein antigens. I. Characterization of the antigen-induced in vitro T cell-dependent proliferative response with lymph node cells from primed mice. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):1048–1053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson W. F., Parish C. R. A procedure for removing red cells and dead cells from lymphoid cell suspensions. J Immunol Methods. 1975 Jun;7(2-3):291–300. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(75)90026-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hersh E. M., Harris J. E. Macrophage-lymphocyte interaction in the antigen-induced blastogenic response of human peripheral blood leukocytes. J Immunol. 1968 Jun;100(6):1184–1194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hünig T. H., Schimpl A., Wecker E. Mechanism of T-cell help in the immune response to soluble protein antigens II. Reconstitution of primary and secondary in vitro immune responses to dinitrophenyl-carrier conjugates by T-cell-replacing factor. J Exp Med. 1977 May 1;145(5):1228–1236. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.5.1228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishell R. I., Dutton R. W. Immunization of dissociated spleen cell cultures from normal mice. J Exp Med. 1967 Sep 1;126(3):423–442. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.3.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North J. R., Kemshead J. T., Askonas B. A. Non-specific factor replaces T cells in an IgG response to soluble antigens. Immunology. 1977 Sep;33(3):321–329. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne D. P., Jr, Katz D. H. Antigen-induced deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in mouse lymphocytes. II. Analysis of the cell populations required for and responding to antigen stimulation in vitro. J Immunol. 1973 Oct;111(4):1176–1182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenberg M. B., Amkraut A. A. Immunogenicity of trinitrophenyl-hemocyanin: production of primary and secondary anti-hapten precipitins. J Immunol. 1966 Sep;97(3):421–430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenberg M. B., Pratt K. L. Antitrinitrophenyl (TNP) plaque assay. Primary response of Balb/c mice to soluble and particulate immunogen. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Nov;132(2):575–581. doi: 10.3181/00379727-132-34264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimpl A., Wecker E., Hünig T. Mechanism of T-cell help in the immune response to soluble protein antigens. I. Evidence for in situ generation and action of T-cell-replacing factor during the anamnestic response to dinitrophenyl keyhole limpet hemocyanin in vitro. J Exp Med. 1977 May 1;145(5):1216–1227. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.5.1216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. H., Jackson L., Paul W. E. T lymphocyte-enriched murine peritoneal exudate cells. I. A reliable assay for antigen-induced T lymphocyte proliferation. J Immunol. 1975 Nov;115(5):1330–1338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeger R. C., Oppenheim J. J. Synergistic interaction of macrophages and lymphocytes in antigen-induced transformation of lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1970 Jul 1;132(1):44–65. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.1.44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmann H., Lefkovits I., Quintáns J. Limiting dilution analysis of helper T-cell function. Immunology. 1975 Jun;28(6):1135–1148. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano A., Schwartz R. H., Paul W. E. Antigen presentation in the murine T-lymphocyte proliferative response. I. Requirement for genetic identity at the major histocompatibility complex. J Exp Med. 1977 Sep 1;146(3):828–843. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.3.828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zollinger W. D., Dalrymple J. M., Artenstein M. S. Analysis of parameters affecting the solid phase radioimmunoassay quantitation of antibody to meningococcal antigens. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 PT2):1788–1798. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


