Abstract
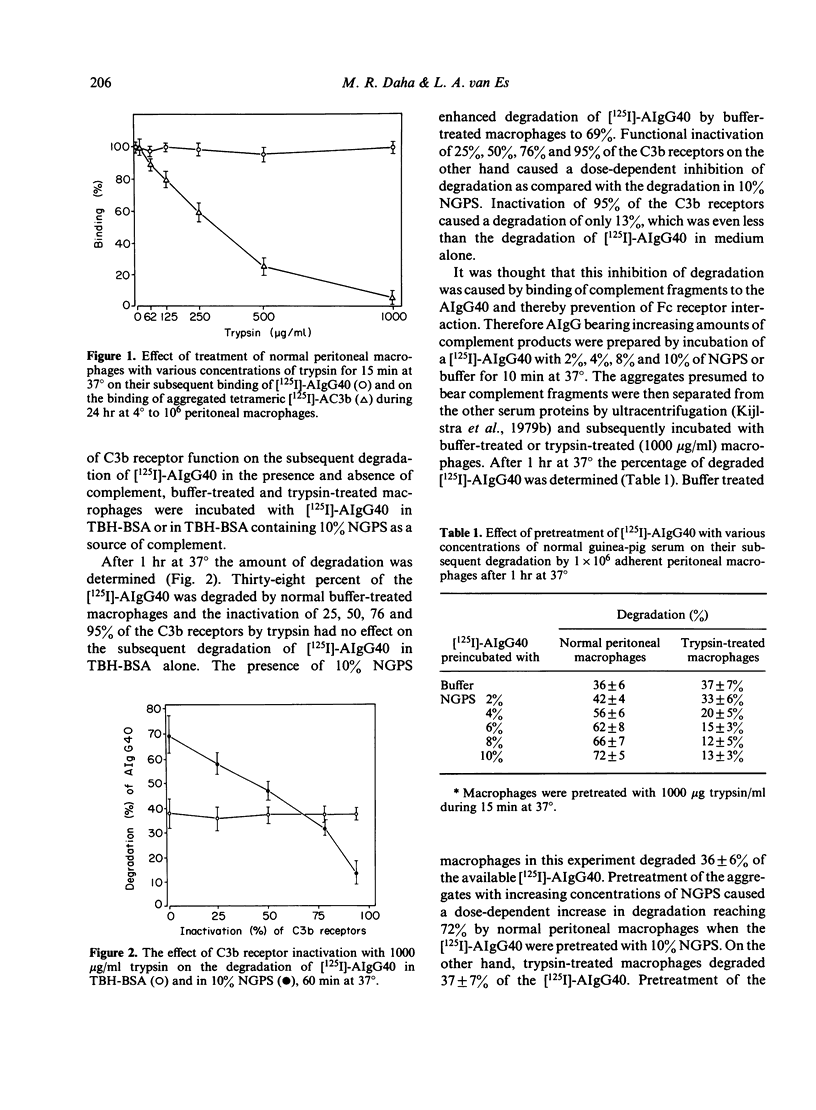
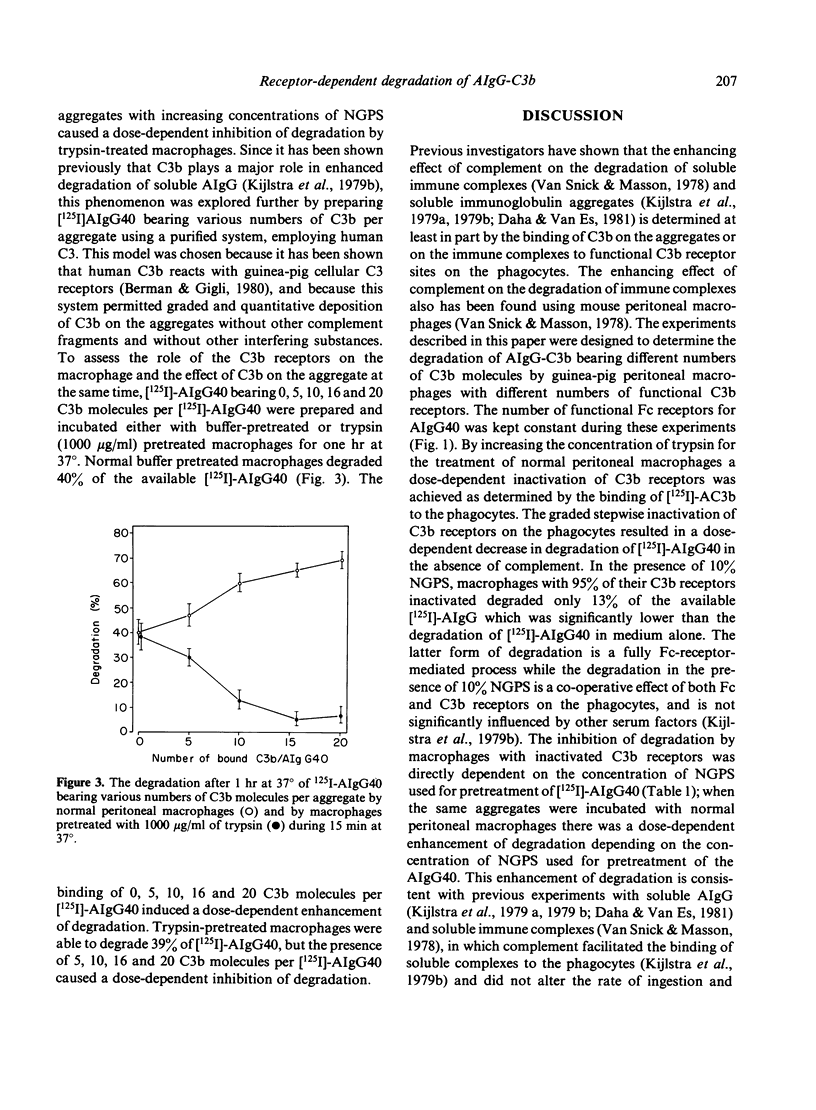
The experiments described in this paper were designed to determine the degradation of soluble IgG aggregates (AIgG) bearing C3b by guinea-pig peritoneal macrophages with different numbers of functional C3b receptors. The number of functional Fc receptors for AIgG containing 40 molecules of IgG per aggregate (AIgG40) were kept constant during these experiments. By increasing the concentration of trypsin for the treatment of normal peritoneal macrophages a dose-dependent inactivation of C3b receptors was achieved as determined by the binding of tetrameric [125I]-C3b([125I]-AC3b). Normal peritoneal macrophages bound 148,500 AIgG40 and 60,300 AC3b per cell. Treatment of the macrophages for 15 min at 37 degrees with incremental amounts of trypsin from 60 to 1000 micrograms/ml did not affect the binding of AIgG40 to macrophages but caused a dose-related loss of up to 95% of AC3b binding, indicating functional inactivation of C3b receptors. Degradation of trichloroacetic acid non-precipitable protein of [125I]-AIgG40 by 10(6) macrophages was 38 +/- 6% in medium alone and 60 +/- 8% in the presence of 10% fresh guinea-pig serum (NGPS) after 60 min at 37 degrees. The inactivation of 25%, 50%, 72% and 94% of C3b receptors by trypsin did not affect the degradation of AIgG40 in medium alone, but decreased degradation from 69% to 58%, 47%, 32% and 13% of AIgG40 respectively, in the presence of 10% GPS. Macrophages (10(6)) in medium alone degraded 40%, 47%, 65% and 68% of AIgG40 bearing 0, 5, 10, 16 and 20 C3b molecules per aggregate, indicating a dose-dependent enhancement of degradation by bound C3b; conversely, inactivation of 95% of C3 receptor on the macrophages resulted in 39%, 30%, 12%, 5% and 6% degradation of these AIgG40-C3b, indicating a dose-related inhibition by aggregate-bound C3b in the absence of cellular C3 receptor. These experiments stress the importance of Fc and C3b receptor co-operation and immune complex bound C3b.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arend W. P., Mannik M. Studies on antigen-antibody complexes. II. Quantification of tissue uptake of soluble complexes in normal and complement-depleted rabbits. J Immunol. 1971 Jul;107(1):63–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENACERRAF B., SEBESTYEN M., COOPER N. S. The clearance of antigen antibody complexes from the blood by the reticuloendothelial system. J Immunol. 1959 Feb;82(2):131–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman B., Gigli I. Complement receptors on guinea pig epidermal Langerhans cells. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):685–690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane C. G., Koffler D. Immune complex disease in experimental animals and man. Adv Immunol. 1973;16(0):185–264. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60298-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daha M. R., Fearon D. T., Austen K. F. C3 nephritic factor (C3NeF): stabilization of fluid phase and cell-bound alternative pathway convertase. J Immunol. 1976 Jan;116(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daha M. R., Van Es L. A. Enhanced alternative complement pathway-dependent degradation of soluble immunoglobulin aggregates by macrophages. Immunology. 1981 Jul;43(3):513–518. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehlenberger A. G., Nussenzweig V. The role of membrane receptors for C3b and C3d in phagocytosis. J Exp Med. 1977 Feb 1;145(2):357–371. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.2.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T., Austen K. F. Properdin: binding to C3b and stabilization of the C3b-dependent C3 convertase. J Exp Med. 1975 Oct 1;142(4):856–863. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.4.856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T., Kaneko I., Thomson G. G. Membrane distribution and adsorptive endocytosis by C3b receptors on human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1981 Jun 1;153(6):1615–1628. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.6.1615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haakenstad A. O., Mannik M. Saturation of the reticuloendothelial system with soluble immune complexes. J Immunol. 1974 May;112(5):1939–1948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hack C. E., Hannema A. J., Eerenberg-Belmer A. J., Out T. A., Aalberse R. C. A C1-inhibitor-complex assay (INCA): a method to detect C1 activation in vitro and in vivo. J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1450–1453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammer G. M., Schur P. H. Binding of circulating immune complexes to human peripheral blood lymphocytes: effect of complement. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1978 Jun;10(2):202–213. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(78)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kijlstra A., Van Der Lelij A., Knutson W., Fleuren G. J., Vanes L. A. The influence of phagocyte function on glomerular localization of aggregated IgM in rats. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 May;32(2):207–217. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kijlstra A., Van Es L. A., Daha M. R. Enhanced degradation of soluble immunoglobulin aggregates by macrophages in the presence of complement. Immunology. 1979 Jul;37(3):673–680. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kijlstra A., van Es L. A., Daha M. R. The role of complement in the binding and degradation of immunoglobulin aggregates by macrophages. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2488–2493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutson D. W., Kijlstra A., Van Es L. A. Association and dissociation of aggregated IgG from rat peritoneal macrophages. J Exp Med. 1977 May 1;145(5):1368–1381. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.5.1368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips-Quagliata J. M., Levine B. B., Quagliata F., Uhr J. W. Mechanisms underlying binding of immune complexes to macrophages. J Exp Med. 1971 Mar 1;133(3):589–601. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.3.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber A. D., Frank M. M. Role of antibody and complement in the immune clearance and destruction of erythrocytes. I. In vivo effects of IgG and IgM complement-fixing sites. J Clin Invest. 1972 Mar;51(3):575–582. doi: 10.1172/JCI106846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Snick J. L., Masson P. L. The effect of complement on the ingestion of soluble antigen-antibody complexes and IgM aggregates by mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Exp Med. 1978 Oct 1;148(4):903–914. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.4.903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


