Fig. 1.
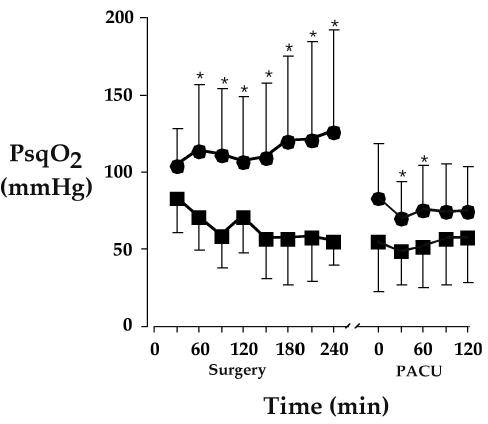
Subcutaneous oxygen tension, the primary determinant of wound infection risk, during surgery and in the postoperative care unit (*P < 0.01) [29]. Tissue oxygenation was measured in a surrogate wound on the upper arm. Intraoperative tissue oxygen partial pressure was doubled by supplemental oxygen (FIO2 = 80% vs. 30%); the effect was less during the postoperative period. Results are expressed as means ± SDs.
