Figure 4.
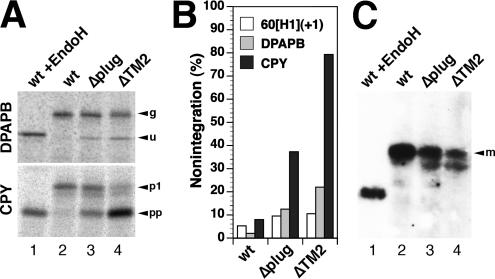
Co- and posttranslational integration defects of Sec61p mutations. Integration of DPAPB as a cotranslational substrate and of CPY as a posttranslational substrate of the Sec61 translocon was analyzed in a Δssh1 background by pulse labeling for 5 min with [35S]methionine, immunoprecipitation, gel electrophoresis, and autoradiography (A). The different products correspond to glycosylated (g) and unglycosylated (u) forms of DPAPB and to the glycosylated first proform (p1) and the unglycosylated pre-pro-form (pp) of CPY. As a control, labeled protein from cells expressing wild-type Sec61p (wt) were analyzed after deglycosylation with endoglycosidase H (EndoH). The unglycosylated forms correspond to nonintegrated polypeptides and were quantified as a fraction of the total in B. In C, the steady-state levels of mature CPY (m) was determined by immunoblot analysis. Equal amounts of cell lysates were analyzed in lanes 2–4.