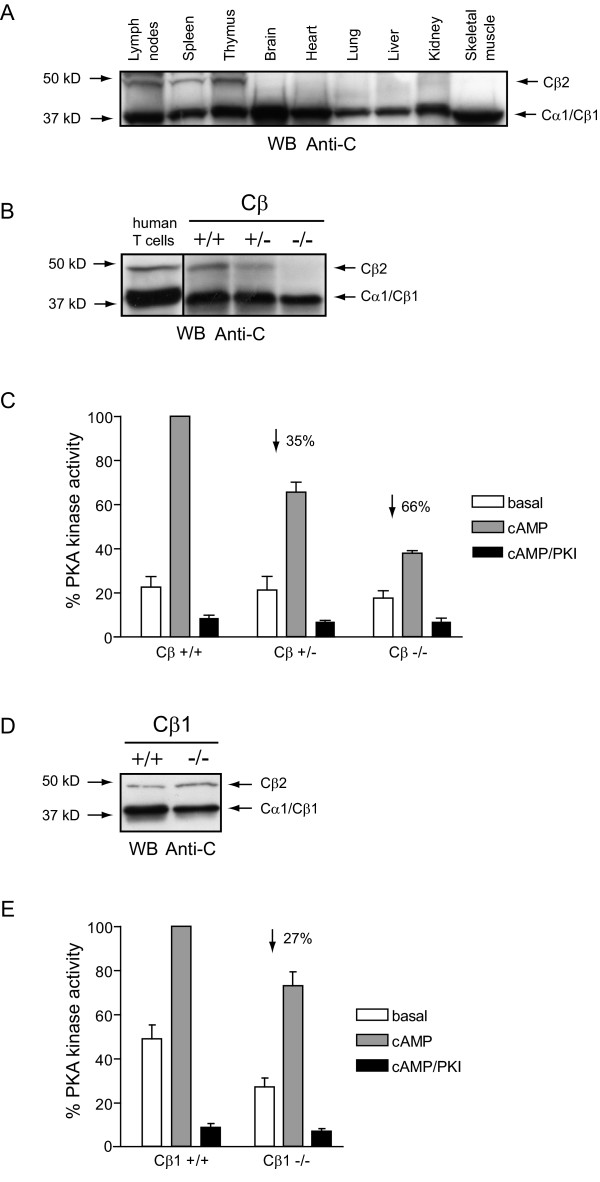
Figure 1.
C subunit identity and PKA specific kinase activity in murine spleen cells. (A) SDS-PAGE (12.5 % gels) and anti-C immunoblotting of lysates (90 μg/lane) from lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, brain, heart, lung, liver, kidney and skeletal muscle from a WT mice. Arrows indicate molecular mass standards (left) and C subunit identities (right). (B) SDS-PAGE (12.5 % gels) and anti-C immunoblotting of cell lysates (60 μg/lane) from human T cells and from wild type (Cβ+/+), Cβ heterozygote (Cβ+/-) and Cβ knockout (Cβ-/-) mice. Arrows indicate molecular mass standards (left) and C subunit identities (right). (C) PKA-specific phosphotransferase activity in spleen lysates (1 μg/ml) isolated from wild type (Cβ+/+), Cβ heterozygote (Cβ+/-) and Cβ knockout (Cβ-/-) mice. Activity was measured in the absence (empty bars, basal) or presence (gray bars, cAMP) of 5μM cAMP or both cAMP and PKI (black bars, cAMP/PKI). Activities in the extracts from the mutant mice are given relative to the activity in the lysates from wild type cell lysate, which are set to 100 %. Bars represent mean activities of three experiments ± standard deviation. Percentage reductions in activities were calculated after subtraction of non specific kinase activity (black bars) and are indicated with an arrow. (D) SDS-PAGE (12.5 % gels) and anti-C immunoblotting of spleen lysates (60 μg/lane) from wild type (Cβ1+/+) and Cβ1 knockout (Cβ1-/-) mice. Arrows indicate molecular mass standards (left) and C subunit identities (right). (E) PKA-specific phosphotransferase activity in spleen lysates (1 μg/ml) from wild type (Cβ1+/+) and Cβ1 knockout (Cβ1-/-) mice were measured and presented as described in C. Bars represent mean activities of three experiments ± standard deviation.