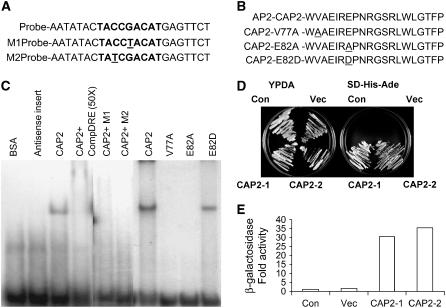
Figure 3.
A, The C-repeat/DRE sequences tested for gel-shift assay are either wild-type version found in the promoter of Arabidopsis RD29A (bold fonts represent 9-bp element) or mutant versions M1 and M2. Monomers are shown, and dimers were used in the experiments. Modified bases are underlined. B, Part of AP2 domains of the wild-type CAP2 and the mutated proteins V77A, E82A, and E82D used in the gel-shift assay. Modified amino acids are underlined. C, Gel-shift assays demonstrating that CAP2 binds to the C-repeat/DRE probe. The probes (1 ng) used in all reactions were 32P-labeled dimers of the oligonucleotides shown in A. Mutated and wild-type recombinant CAP2 proteins, described in B, were expressed in E. coli DH5α as GST-fused proteins and purified by GST-agarose columns. CAP2 cDNA was cloned in antisense orientation and purified similarly to make antisense protein. D, Activation of two reporter genes in yeast by CAP2. CAP2 cDNA cloned in yeast expression vector to produce CAP2 protein fused with GAL4 DNA BD was used for transformation into a yeast strain carrying three reporter genes, HIS3, ADE2, and LacZ, under the control of the GAL4 promoter. Yeast colonies carrying no vector (Con), vector only (Vec), and two transformants (CAP2-1 and CAP2-2) carrying CAP2 cDNA cloned in vector were grown on YPDA and on synthetic medium lacking His and Ade. E, Activation of the third reporter gene as in D is shown by β-galactosidase assay of the transformants presented as fold increase in activity.