Figure 1.
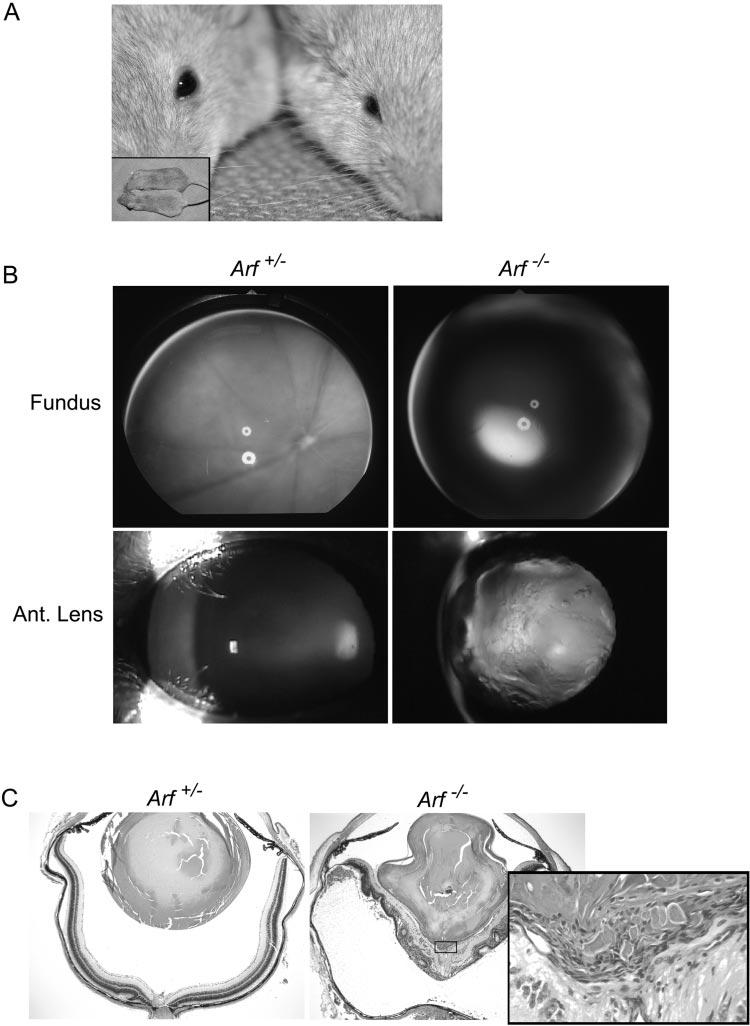
Clinical and pathologic features of severe PHPV in Arf−/− mouse. (A) Photograph of representative Arf+/+ (left) and Arf−/− (right) mice showing microphthalmic appearance without apparent difference in overall body size (inset). (B) Fundoscopic (top) and slit lamp images (bottom) are normal in Arf+/− eye (left). Dens lens opacity obscures fundoscopic view in Arf−/− eye (right). (C) Photomicrographs of hematoxylin and eosin–stained sections of eyes from Arf+/− (left) and Arf−/− (right) mice used for (B). Note misshapen lens, dysplastic neuroretina detached from pigment epithelium in Arf−/− mouse. Inset: high magnification of fibrovascular retrolental mass (box) directly apposed to posterior lens and inner neuroretina. Original magnification: ×40; inset: ×400.
