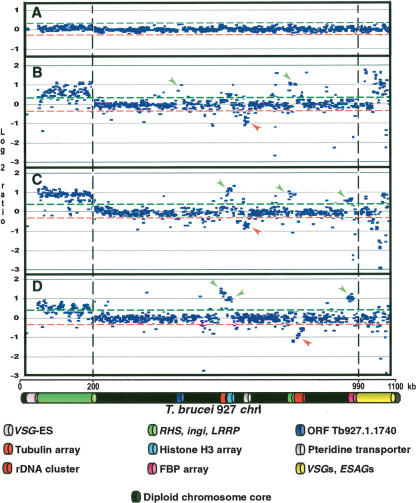
Figure 1.
Copy number polymorphism in chromosome I homologs of T. brucei, assayed by comparative genomic hybridization to a microarray of T. brucei 927 chrIa DNA fragments. (A) Co-hybridization of Tb927 genomic DNA differentially labeled with Cy5 and Cy3. (B) Cohybridization of differentially labeled Tb247 and Tb927 genomic DNA; (C) Tb427 and Tb927; (D) T.b. gambiense-M (Tbg-M) and Tb927. (Green and red lines) Two SD from the zero line in experiment A. Location of a fragment above the green line indicates copy number amplification in the test genome relative to Tb927; below the red line indicates DNA loss or sequence divergence in the test genome. (Vertical discontinuous lines) Subtelomere limits. Left subtelomere contains primarily retrotransposons (ingi) and gene families RHS and LRRP. Right subtelomere contains primarily genes involved in antigenic variation (VSGs) and associated genes (ESAGs). (VSG-ES) A VSG expression site; (FBP) a gene containing an F-box motif. (Green arrows) Gains of DNA; (red arrows) losses of DNA. Tandemly repeated gene coordinates: Tubulin array Tb927.1.2330–2410; Histone H3 array Tb927.1.2430–2550; Pteridine transporter array Tb927.1.2820, 2850, 2880; FBP array Tb927.1.4540–4650.