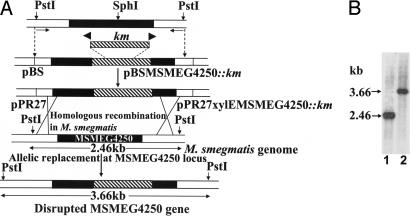
Fig. 1.
Generation of M. smegmatis ΔMSMEG4250 by targeted disruption. (A) Schematic representation of the genetic structures obtained during the construction of the mutation in MSMEG4250 of M. smegmatis. Black boxes indicate coding sequence of MSMEG4250. Hatched regions represent the intragenic DNA fragment replaced with a Km cassette from pUC4K. The locations of primers for PCR are indicated by small arrows. Homologous recombination and selection for Km and sucrose resistance and xylE resulted in colonies with a disrupted MSMEG4250, which remained white upon spraying with catechol (XylE−). (B) Southern blot hybridization was performed on genomic DNA prepared from M. smegmatis mc2155 cells (lane 1) and the candidate mutant colony (lane 2). DNA was restricted with PstI and probed with the PCR product generated with the primers used in the initial step.