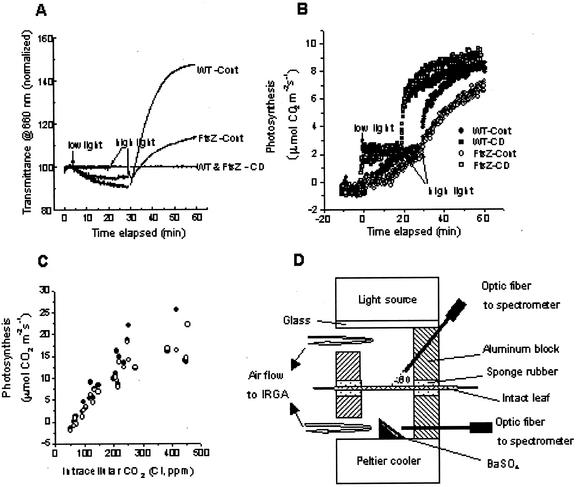
Figure 4.
Changes in leaf transmittance (A) and CO2 exchange rates (B) in tobacco leaves measured at 660 nm. Dark-adapted intact leaves were first illuminated under low light (40 μmol m−2 s−1), then immediately followed by high light (750 μmol m−2 s−1). WT-Cont, Wild type treated with DW; FtsZ-Cont, transgenic plant treated with DW; WT & FtsZ-CD, wild-type and transgenic plants treated with 5 μm cytochalasin D; wild type (▪ and ●); transgenic plant (□ and ○). C, Net photosynthesis (Pn) versus intracellular CO2 concentration (Ci) in attached leaves of the wild-type (●) and transgenic (○) tobacco plants. The light intensity for CO2 exchange was 750 μmol m−2 s−1 and leaf temperature was 25°C ± 1°C. D, Schematic diagram of a Parkinson leaf chamber modified for the simultaneous measurement of optical properties and gas exchange. Two optic fibers were inserted into the chamber to collect lights reflected directly from an intact sample and from a small block coated with barium sulfate mounted on the bottom of the chamber, respectively.