Figure 4.
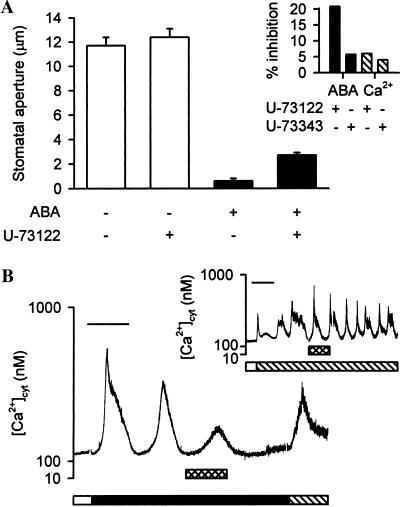
ABA-induced stomatal closure and oscillations in guard-cell [Ca2+]cyt are inhibited by U-73122. (A) Isolated epidermis of C. communis was incubated in Mes/KCl for 3 h under conditions promoting stomatal opening and then transferred to Mes/KCl containing no ABA (open bars) or 1 μM ABA (solid bars) for 15 min in the absence or presence of 1 μM U-73122. Subsequently, the epidermis was incubated for a further 45 min in fresh Mes/KCl containing no or 1 μM ABA, respectively, in the absence of U-73122. Values are the means of 80 measurements ± SEM. (A Inset) Percentage inhibition of 1 μM ABA-induced (solid bars) or 1 mM external Ca2+ ([Ca2+]ext)-induced (hatched bars) stomatal closure by 1 μM U-73122 or U-73343. ([Ca2+]ext is a potent closing stimulus that induces oscillations in guard-cell [Ca2+]cyt; ref 14.) Values are calculated from the means of 180 measurements. (B) Fura-2-loaded guard cells of open (>6 μm) stomata of C. communis were perfused with Mes/KCl, and the resting level of [Ca2+]cyt was determined (open bar). Subsequently, guard cells were perfused with Mes/KCl containing 1 μM ABA (solid bar). After the characteristic oscillations in [Ca2+]cyt had been established, cells were given a 15-min pulse of 1 μM U-73122 (crosshatched bar). Perfusion with Mes/KCl containing 1 mM CaCl2 in the absence of ABA (hatched bar) at the end of each experiment showed that cells were still viable and were capable of maintaining Ca2+ homeostasis after exposure to U-73122. A representative trace is shown. (Bar = 15 min.) (B Inset) The effect of 1 μM U-73122 on oscillations in guard-cell [Ca2+]cyt in response to [Ca2+]ext. Resting [Ca2+]cyt was determined in fura-2-loaded guard cells of open (>6 μm) stomata of C. communis at the start of each experiment, during perfusion with Mes/KCl (open bars). Subsequently, guard cells were perfused with Mes/KCl containing 1 mM CaCl2 (hatched bar). U-73122 was given as a 15-min pulse (crosshatched bar). A representative trace is shown. (Bar = 15 min.)