Figure 8. Proposed roles of RecQ helicases in telomere maintenance.
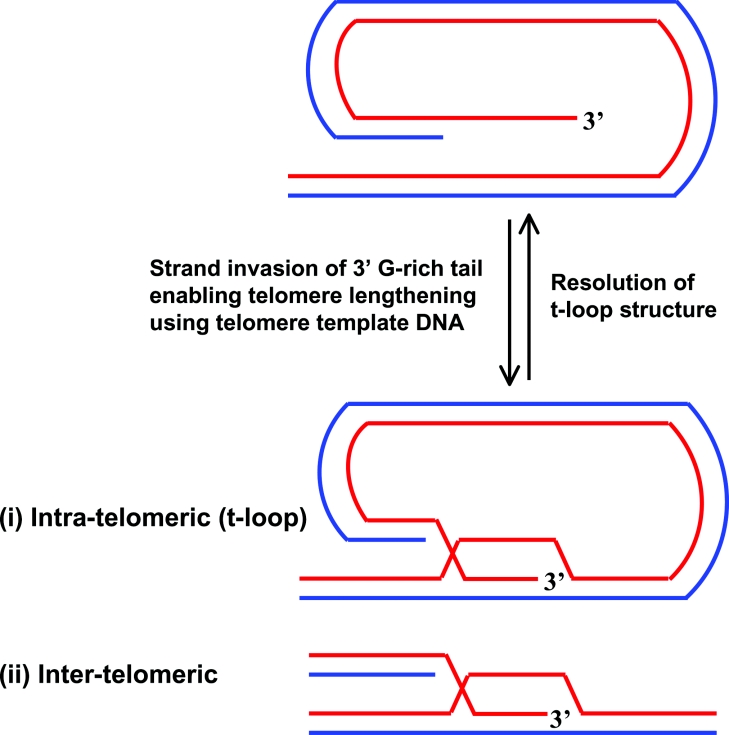
T-loops are created through strand invasion of the 3′ telomeric overhang into the duplex region of the telomere. ALT is a recombination-based pathway that operates in telomerase-deficient cells. This pathway might involve RecQ- and TRF2-mediated strand invasion of the 3′ G-rich tail, enabling the telomere to be lengthened by using telomeric DNA as a template. The telomeric template DNA can originate from two sources: (i) intra-telomeric, where the t-loop is used to prime DNA synthesis, or (ii) inter-telomeric, where the DNA is copied from another telomere or telomeric sequence that exists as extrachromosomal DNA. Additionally, maintenance of telomere length might require a RecQ helicase (e.g. BLM or WRN) to resolve the D-loop structure at the t-loop or unwind a G-quadruplex in the 3′ G-rich tail.