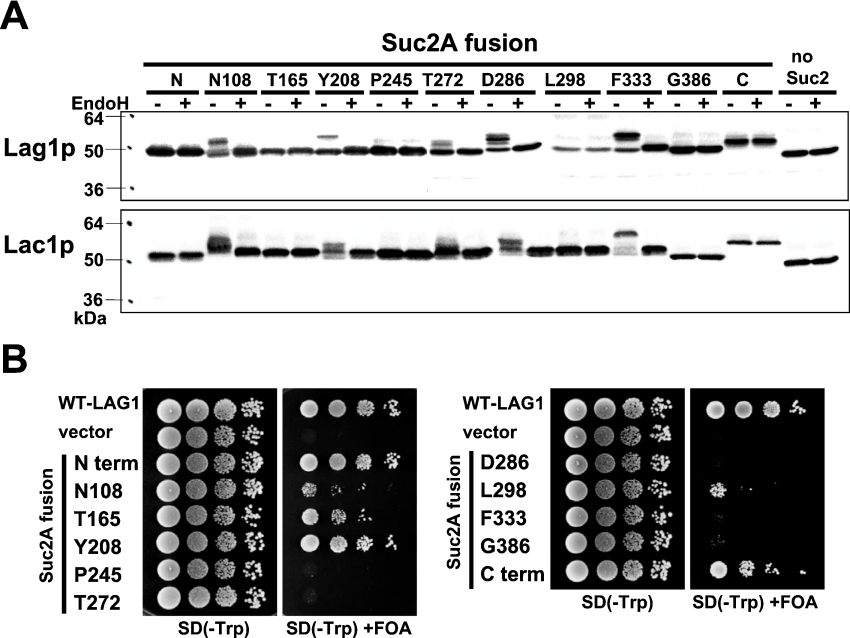
Figure 2. Topology determination by insertion of glycosylation sites.
(A) The glycosylation status of the topological reporter Lag1–Suc2A and Lac1–Suc2A fusion proteins. RH382 cells were transformed with plasmids 1777–1798 to express the Lag1–Suc2A and Lac1–Suc2A fusion proteins. The numbers and amino acids represent the amino acid residues of Lag1p and Lac1p before which the 53-amino-acid cassette was inserted. Total cell lysates were prepared from the transformants, treated with or without endo H for 90 min at 37 °C, and resolved on 12% (w/v) polyacrylamide gels. The Lag1 and Lac1 proteins were detected by immunoblotting using anti-FLAG antibodies. (B) Functional complementation of lag1Δ lac1Δ cells by Lag1–Suc2A fusion proteins. lag1Δ lac1Δ double deletion mutant cells transformed with pRS416-LAG1 (LAG1 on uracil-based plasmid) (RH6602) were transformed with pRS414-LAG1-SUC2AN (LAG1-SUC2A fusion constructs on tryptophan-based plasmid) (plasmids 1799–1809). The transformants were diluted to a final concentration of 1×107 cells/ml, and 10 μl of 10-fold dilutions were spotted on SD (−Trp)- and SD (−Trp)-containing 5-FOA plates. The plates were incubated at 30 °C for 3 days. The deletion mutants transformed with wild-type LAG1 (plasmid 1751) and vector without insert (plasmid 1750) were used as controls.