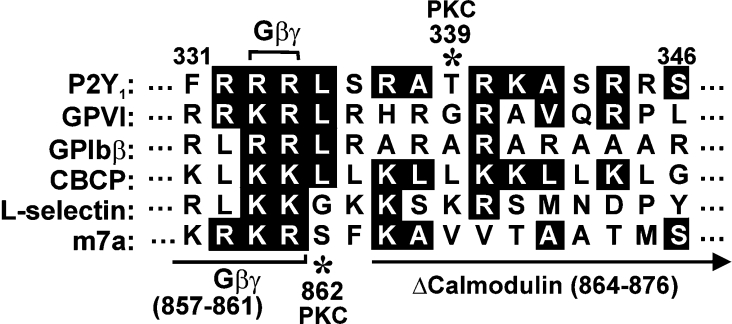
Figure 1. Comparison of calmodulin-binding sequences.
Juxtamembrane calmodulin-binding sequence within the P2Y1 C-terminal cytoplasmic tail, compared with known calmodulin-binding sequences in platelet GPVI [15–17], GPIbβ [14], a non-physiological calmodulin-binding control peptide that forms amphipathic α-helix [20], leucocyte adhesion receptor, L-selectin [21] and the G-protein-coupled glutamate receptor m7a [22]. Identical residues or conservative substitutions are highlighted. The Gβγ-binding region (residues 857–861) and the site of a deletion (residues 864–876) that blocks calmodulin binding are shown on the m7a sequence [22] compared with the G-protein-binding site at Arg333/Arg334 of P2Y1 [23]. Asterisks show known PKC-dependent phosphorylation sites in m7a (Ser862) [24] and P2Y1 (Thr339) [25,26].