Figure 5.
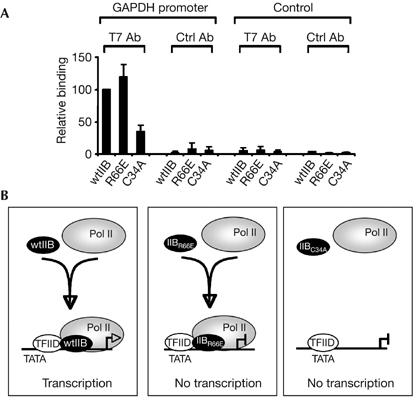
Assembly of TFIIB amino-terminal mutants at the promoter in vivo. (A) 293 cells were transfected with 2 μg of a plasmid driving the expression of wild-type TFIIB or the indicated derivative. After 24 h, chromatin immunoprecipitation was performed with anti-T7 antibodies to specifically isolate chromatin associated with the transfected TFIIB derivatives. Real-time quantitative PCR was performed with primers to amplify the GAPDH promoter region (left) or a control non-promoter region (right). Results shown are the average of three independent experiments, each normalized to input. (B) A model of TFIIB–Pol II association with the promoter is shown (discussed in the text). Assembly of wild-type TFIIB (wtIIB) and the TFIIB mutants (IIBR66E and IIBC34A) is depicted. GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; Pol II, polymerase II; TFIIB, general transcription factor IIB.
