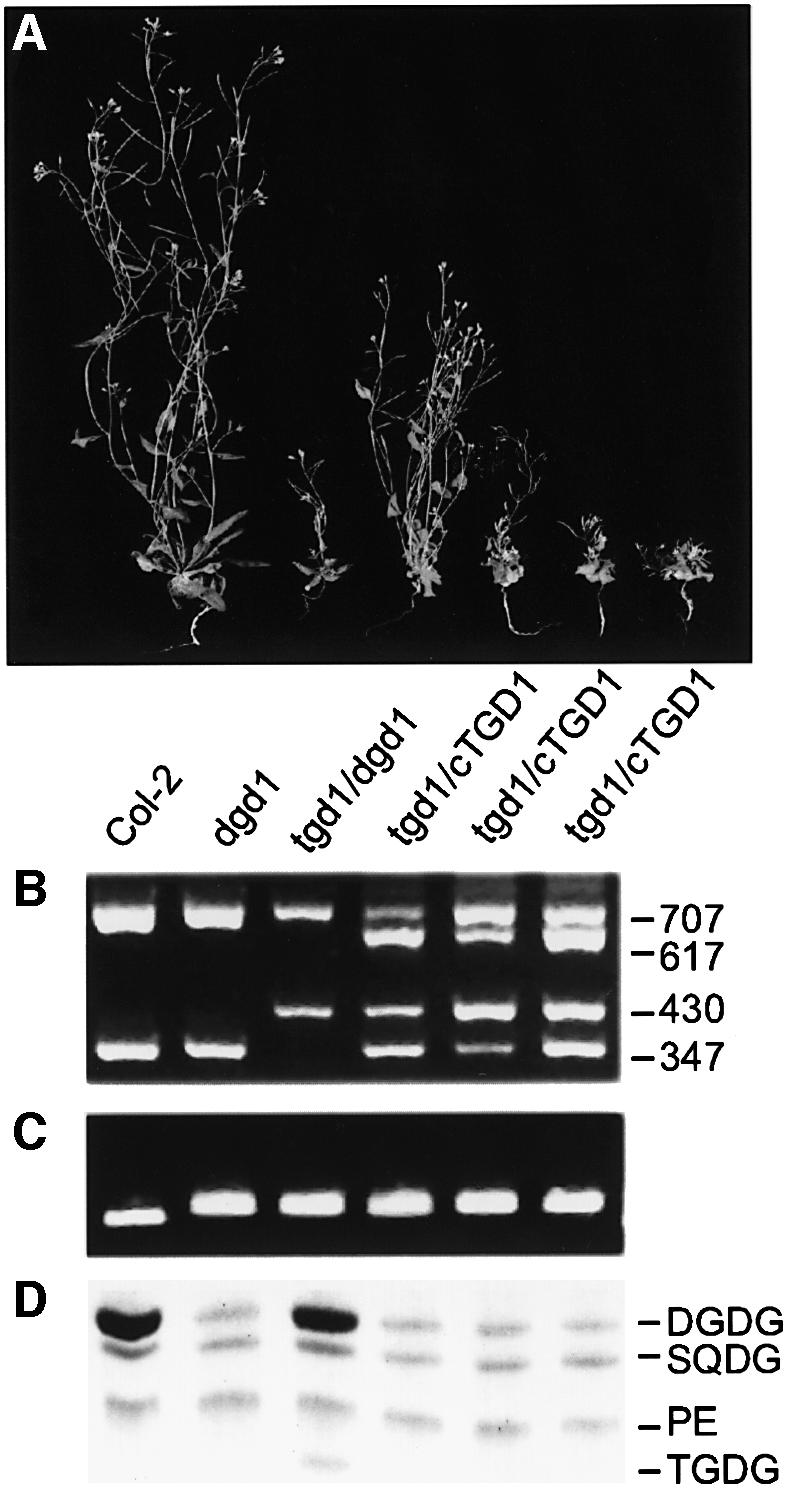
Fig. 7. Complementation of the tgd1-1 mutation by the TGD1 cDNA. (A) Growth habit of wild type, the dgd1 homozygous mutant, the homozygous tgd1-1/dgd1 double mutant and three homozygous tgd1-1/dgd1 double mutants carrying the TGD1 cDNA in trans (from left to right as indicated). (B) Genotyping at the TGD1 locus using a CAPS marker. Fragment sizes are indicated and are diagnostic as follows: 707 bp genomic locus-derived fragment; 617 bp cDNA-specific fragment; 430 bp fragment specific for the mutant tgd1-1 genomic locus; and 347 bp fragment specific for the genomic wild-type locus, but also present in cDNA. (C) Genotyping at the DGD1 locus using a dCAPS marker. The longer fragment is diagnostic for the presence of the dgd1 mutation. (D) Lipid phenotype. A section of a linear TLC is shown. Lipids are: DGDG, digalactosyldiacylglycerol; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; SQDG, sulfoquinovosyldiacylglycerol; TGDG, trigalactosyldiacylglycerol.
