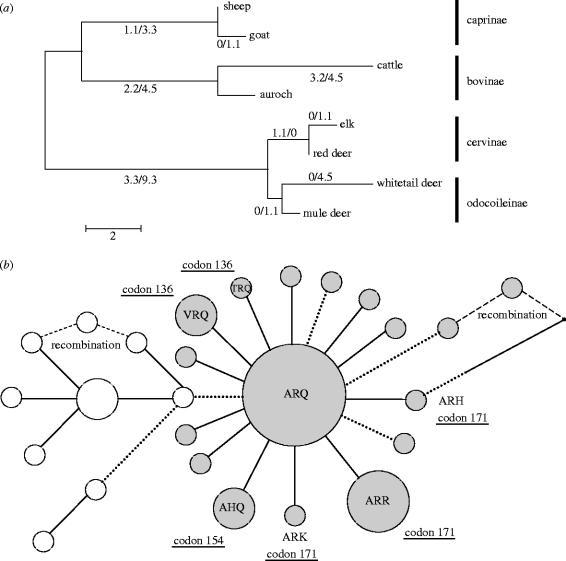
Figure 1.
(a) PRNP coding region evolution within the ruminant phylogeny. Branches are drawn in proportion to their lengths, defined as the number of sequence differences per gene. The maximum likelihood estimates of the number of nonsynonymous and synonymous substitutions are shown for each branch (e.g. 1.1 nonsynonymous and 3.3 synonymous substitutions on the branch leading to the caprinae). The excess of synonymous substitutions is consistent with purifying selection. (b) PRNP coding region haplotype networks for sheep (filled circles) and goats (open circles). Haplotype frequency is proportional to the circle diameter. Substitutions affecting codons 136, 154 and 171 are indicated. Nonsynonymous changes are indicated by solid lines and synonymous substitutions by dotted lines. Note the excess of nonsynonymous substitutions. The number of substitutions that differentiate two haplotypes is indicated by branch length. Nearly all branches represent a single substitution.