Figure 2.
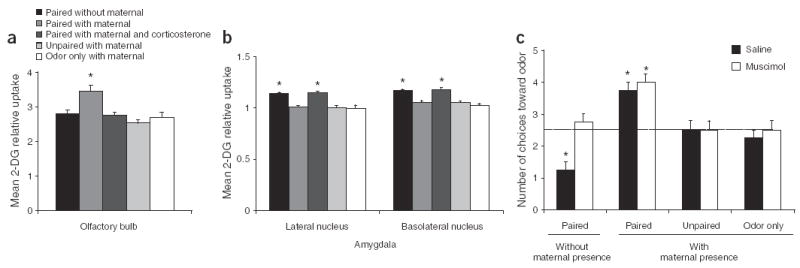
Maternal presence activates a non-amygdala dependent odor-shock circuit and yields odor preference, (a) Olfactory bulb activity during odor-shock acquisition was assessed by relative 14C 2-deoxyglucose (14C 2-DG) uptake. Enhanced uptake was found in pups subjected to paired odor-shocks with maternal presence that expressed an odor preference, (b) Activity in the basolateral and lateral nuclei of the amygdala were enhanced during odor-shock presentation only without maternal presence, as assessed by relative 14C 2-DG uptake. Additional amygdala nuclei and a representative 14C 2-DG/Nissl-stained amygdala section are shown in Supplementary Figs. 1 and 2, respectively. (c) Reversibly silencing the amygdala with the GABA agonist muscimol disrupted the odor aversion learning in pups subjected to odor-shock pairings without maternal presence but had no effect on the pups subjected to odor-shock pairings with maternal presence. *P < 0.05. Error bars represent s.e.m.
