Figure 3.
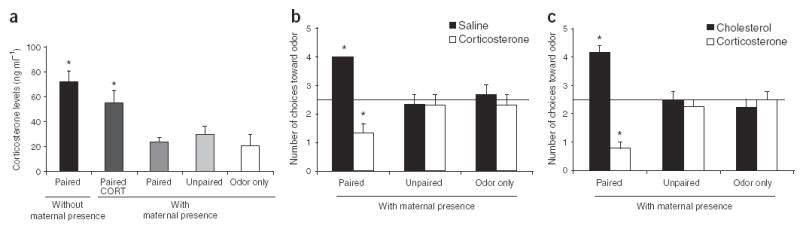
Assessment of the association between corticosterone, learning and the amygdala, (a) Radioimmunoassay (RIA) corticosterone levels were low in pups receiving shock with maternal presence, but high in those receiving shock without maternal presence, (b) Pups subject to paired odor-shock with maternal presence were given systemic corticosterone 30 min before conditioning. These pups showed odor aversion learning, (c) Intra-amygdala corticosterone permitted these pups to learn an odor aversion. *P < 0.05. Error bars represent s.e.m.
