Figure 2.
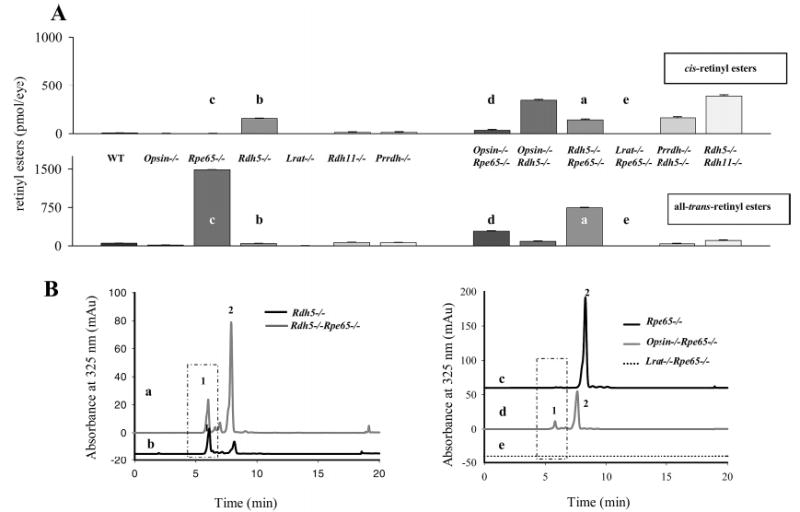
Retinyl esters in the eyes of mice of different genetic backgrounds. (A) All-trans- and cis-retinyl esters in mice of different genetic backgrounds. Retinoids were extracted from 6-week-old eyes and separated on normal-phase HPLC as described in Experimental Procedures. (B) Chromatographic separation of all-trans- and cis-retinyl esters from (a) Rpe65−/−, (b) opsin−/−Rdh65−/−, (c) Lrat−/−Rpe65−/−, (d) Rdh5−/−Rpe65−/−, and (e) Rdh5−/− mice. Retinoids were extracted from 6-week-old eyes and separated on normal-phase HPLC. The box represents cis-retinyl esters (>90% 13-cis-retinyl esters) also indicated as peak 1. Peak 2 represents all-trans-retinyl esters. The mice were reared under dim red light.
