Figure 8.
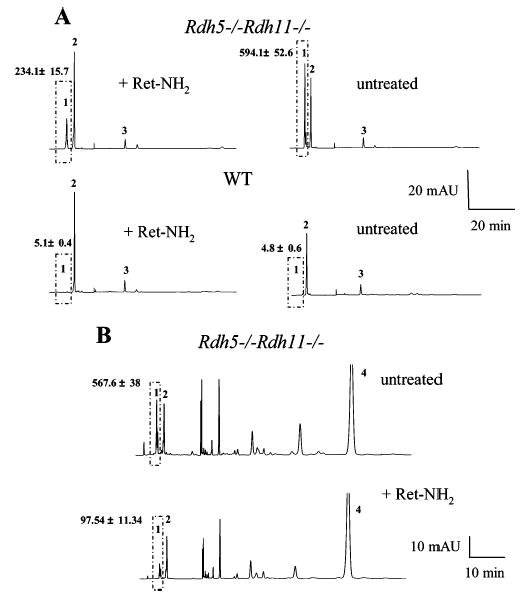
Effects of Ret-NH2 on 13-cis-retinyl ester production. (A) Effects of Ret-NH2 on 13-cis-retinyl ester production induced by light. Mice were dark adapted for 48 h, gavaged with 1 mg of Ret-NH2, and then exposed to intense light for 3 min at 500 cd·m−2, 24 h postgavage. A representative chromatogram is shown, and the average data from three mice are indicated with standard deviation above the ester peaks (mean ± SD). The box represents cis-retinyl esters (>90% 13-cis-retinyl esters). (B) Effects of Ret-NH2 on 13-cis-retinyl ester production from injected all-trans-retinol. Mice were dark adapted for 48 h and gavaged with 1 mg of Ret-NH2. After 24 h, 400 nmol of all-trans-retinol in 1 μL of DMSO was intravenously injected. A representative chromatogram is shown, and the average data from three mice are indicated with standard deviation above the ester peaks (mean ± SD). The box represents cis-retinyl esters (>90% 13-cis-retinyl esters). Peaks 1, 2, 3/3′, and 4 represent cis-retinyl esters, all-trans-retinyl esters, 11-cis-retinal oximes, and all-trans-retinol, respectively.
