Fig. 8.
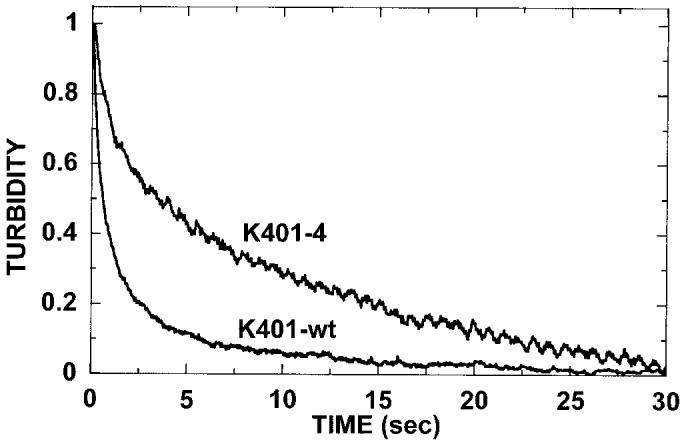
ATP-promoted dissociation at low salt. The preformed Mt·K401-wt and Mt·K401-4 complexes (3 μm K401-4, 2.9 μm tubulin) were rapidly mixed with 1 mm MgATP, and turbidity was monitored in the stopped-flow apparatus. For this experiment, additional salt was not added to the ATP syringe to evaluate whether the mutant motor detaches directly after ATP hydrolysis (Scheme 2, path 1) or the mutant motor follows path 2 and results in an intermediate with both heads bound to the microtubule and at the same stage in the ATPase cycle (Scheme 2, path 2). The dissociation kinetics of K401-wt at 1.7 s−1 indicate that the wild type motor is in association with the microtubule for 0.6 s (transit time = 1/kobs). For K401-4, the dissociation kinetics are biphasic with the exponential phase at 1.4 s−1 (transit time = 0.7 s) followed by a second slower phase at 0.1 s−1.
