Fig. 5.
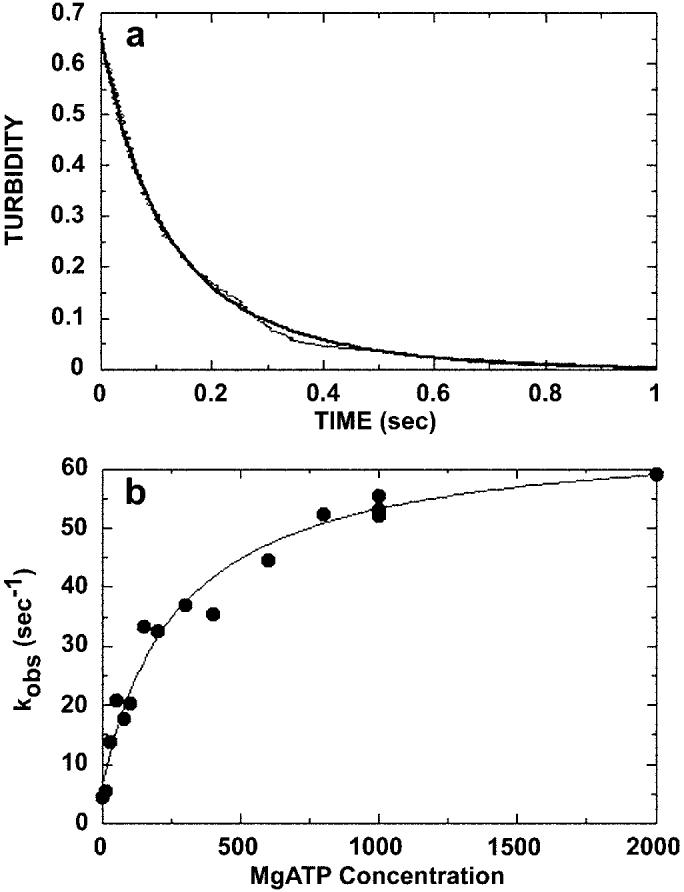
ATP-promoted dissociation of the Mt·K401-4 complex. The preformed Mt·K401-4 complex (3 μm K401-4, 2.9 μm tubulin) was rapidly mixed with varying concentrations of MgATP (10 μm to 2 mm) plus 100 mm KCl, and turbidity was monitored in the stopped-flow apparatus. The salt was added to slow rebinding of K401-4 to microtubules after dissociation. A, a representative stopped-flow record (average of six traces) for 1 mm MgATP. The smooth line is the fit of the data to a double exponential. The kobs of the initial exponential phase was 49.4 ± 0.8 s−1. The second exponential phase was too slow to be considered on the pathway. B, the rate constant of the exponential phase for each transient was plotted as a function of MgATP concentration. The data were fit to a hyperbola, providing the maximum dissociation rate constant k+3 of 59.8 ± 2.9 s−1 and K0.5, ATP = 280 ± 57.1 μm.
