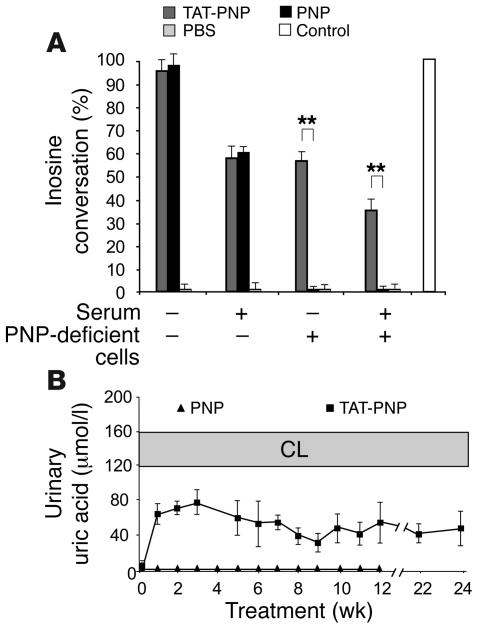
Figure 5. Anti-PNP antibodies neutralize TAT-PNP but do not prevent intracellular TAT-PNP transduction.
(A) Serum from PNP–/– mice treated with TAT-PNP, which contained antibodies to PNP that neutralized PNP enzyme activity, yet TAT-PNP still delivered active enzyme into PNP-deficient cells. Enzyme activity (14C-labeled inosine conversion) was measured after 20 minutes’ incubation of TAT-PNP or nonfused PNP, both at 0.1 U/ml, or PBS in the absence or presence of serum containing antibodies to TAT-PNP (diluted 1:100). Following similar incubation in the absence or presence of 2 × 105 PNP-deficient cells, activity was measured in the cell pellets. Results are representative of 3 independent experiments and are presented relative to the activity in normal control cells. **P < 0.005. (B) In spite of increasing concentrations of antibodies to TAT-PNP during treatment of PNP–/– mice with TAT-PNP, uric acid production (which is dependent on active PNP in vivo) was not affected. Twenty-four hours or later after injecting PNP–/– mice with TAT-PNP (squares), uric acid concentrations were measured in the urine and compared with uric acid from PNP–/– mice treated with nonfused PNP (triangles). Results (converted to μmol/l) are mean ± SD of urine samples collected from 6–15 mice and are compared with normal control littermates.