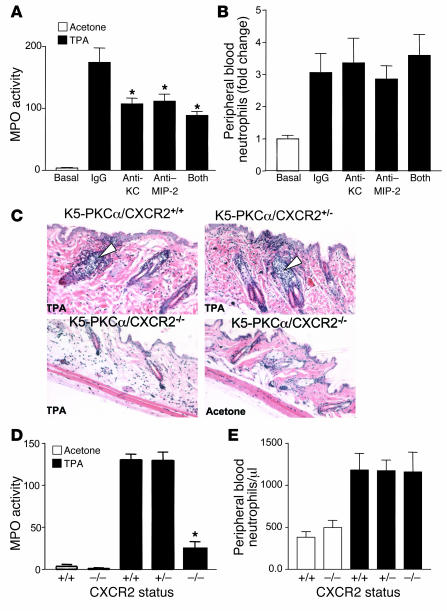
Figure 4. Blocking CXCR2 ligands or CXCR2 deficiency prevents neutrophil infiltration in the skin of K5-PKCα mice.
A single dose of TPA (1 μg) in acetone was applied to the shaved backs of K5-PKCα mice that had been injected intravenously with either control IgG, KC-neutralizing antibodies, MIP-2–neutralizing antibodies, or a combination of KC- and MIP-2–neutralizing antibodies. Skin was collected 6 hours later, and MPO activity was determined (A). Blood was collected at sacrifice, and the number of peripheral blood neutrophils was determined from differential wbc counts (B). For A and B, bars represent the mean ± SEM for 4 animals, and results are representative of 4 experiments. *P < 0.05 versus IgG control group. (C) K5-PKCα mice expressing CXCR2 (K5-PKCα/CXCR2+/+), K5-PKCα mice heterozygous for CXCR2 (K5-PKCα/CXCR2+/–), and K5-PKCα mice deficient for CXCR2 (K5-PKCα/CXCR2–/–) were TPA painted; skin was collected 6 hours later, and sections were stained with H&E. White arrowheads show early stage of neutrophil infiltration into the hair follicles. MPO was determined in skin extracts from the mouse groups depicted in C (D) as well as peripheral blood neutrophil counts (E). For D and E, bars represent the mean ± SEM for 7 animals, and results are representative of 2 experiments. *P < 0.05 versus TPA-treated K5-PKCα/CXCR2+/+ group.