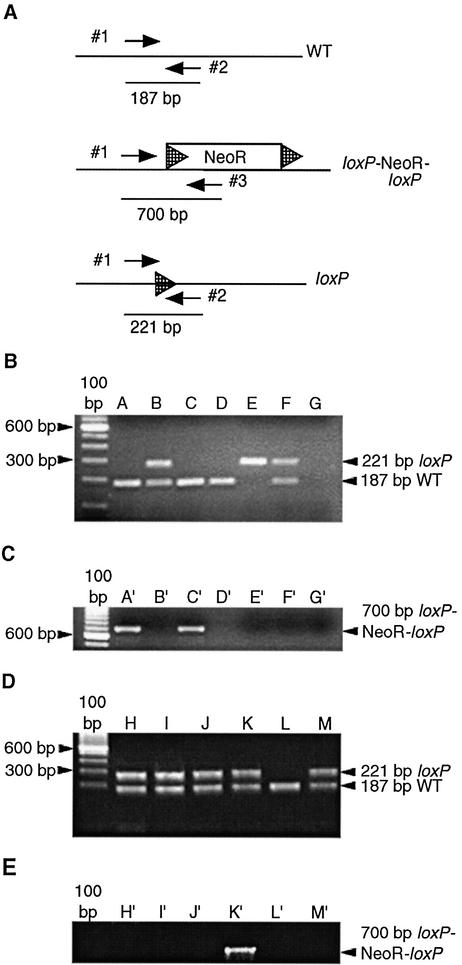
Figure 2.
Location of the PCR primers and detection of various alleles. (A) Primers used to detect the wild-type allele (WT) and the deleted loxP-flanked NeoR allele are labeled 1 and 2. These primers amplify a 187 bp wild-type fragment. Primers 1 and 2 will also amplify the deleted NeoR allele (loxP), which has a residual 34 bp loxP site remaining after Cre-mediated excision of the NeoR gene has occurred. In this case, a 221 bp fragment is amplified. This PCR was designed so that the undeleted loxP-flanked NeoR allele would not amplify if present. Primers 1 and 3 amplify a 700 bp fragment when the loxP-flanked NeoR gene (loxP–NeoR–loxP) is present. NeoR indicates neomycin resistance gene and hatched arrowheads indicate loxP sites. (B) PCR results demonstrating amplification of the 187 bp wild-type allele and the 221 bp deleted loxP allele in tail DNA. (C) PCR amplification of the intact 700 bp loxP–NeoR–loxP allele in tail DNA from the same animals shown in (B). Lanes A and A′ represent the female breeder. Lanes B and B′ represent a Cre(+) male offspring of a mating between the animal in lane A and the Cre(+) founder. Lanes C and C′ represent a female carrying a wild-type allele and a loxP–NeoR–loxP allele. The animal in lanes B and B′ was mated to the animal in lanes C and C′ and the genotypes of the offspring are shown in lanes D–F and D′–F′. Lane D represents a homozygous wild-type mouse, lane E represents a mouse carrying two loxP alleles and lane F represents a mouse with both a wild-type and a loxP allele. Lanes G and G′ represent the negative control PCR in the absence of genomic DNA. (D) PCR results demonstrating amplification of the 187 bp wild-type allele and the 221 bp deleted loxP allele in DNA isolated from the liver (lane H), testes (lane I), tail (lane J) and kidney (lane K) of the F1 mouse shown in (B), lane B. (E) PCR amplification of DNA isolated from the liver (lane H′), testes (lane I′), tail (lane J′) and kidneys (lane K′) of the F1 mouse in (B), lane B. Lanes L, L′, M and M′ represent control amplifications of tail DNA isolated from a wild-type mouse and a mouse carrying both the wild-type and deleted loxP alleles, respectively.