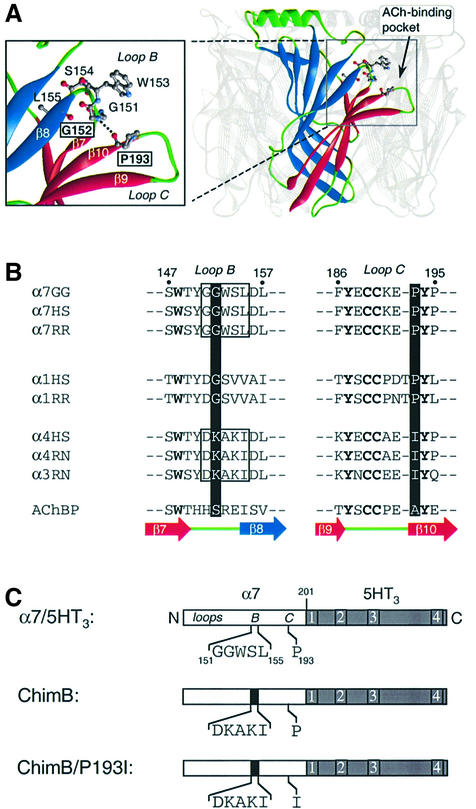
Fig. 1. (A) Three-dimensional model of the extracellular domain of α7 receptor based on the crystal structure of AChBP (Brejc et al., 2001) by comparative modeling (Le Novère et al., 2002). For clarity, one subunit of the pentamer is highlighted. Each subunit is folded in a twisted β-sandwich motif composed of the inner (blue) and outer (red) β-sheets. Nomenclature as described (Unwin et al., 2002). In the enlarged view, a plausible H-bond between G152 and P193 (dotted line) links loop B (fragment 151–155) and the β-hairpin of loop C (fragment 186–195), thus connecting the inner and outer β-sheets at the level of the ACh binding site. (B) Aligned sequences of loops B and C of neuronal (α7, α4 and α3) and muscle (α1) nAChRs: GG, Gallus gallus; HS, Homo sapiens; RR, Rattus norvegicus; AChBP, acetylcholine binding protein. The corresponding strands from the AChBP structure are also indicated under the sequence alignment (Brejc et al., 2001). (C) Schematic representation of the chick α7 ECD (white box) of the chimera α7/5HT3. In this chimera, amino acids beyond residue 201 (gray box) correspond to those of the 5HT3 receptor sequence (Eiselé et al., 1993). The five amino acids of loop B (segment 151–155) and P193 of the wild-type α7/5HT3 are indicated. The microchimera ChimB corresponds to the homologous substitution of rat α4 sequence (black box) loop B, whereas ChimB/P193I corresponds to the same microchimera plus the single mutant P193I in loop C.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.