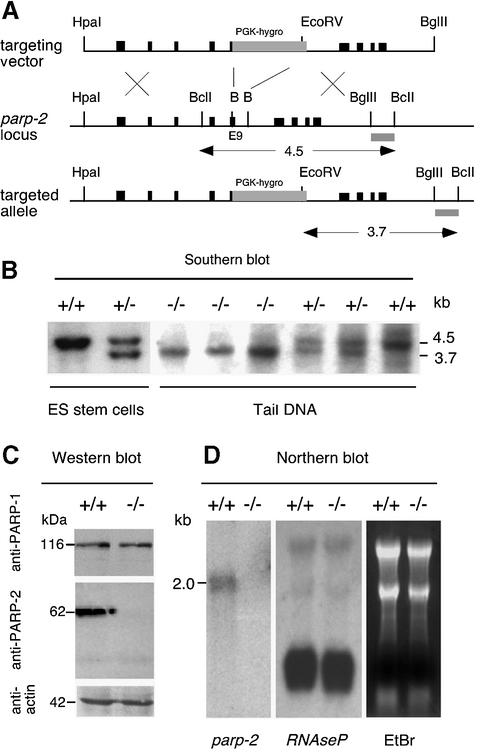
Fig. 1. Targeted disruption of parp-2. (A) Map of the parp-2 murine genomic locus and targeting vector. Exons are indicated by black boxes and the position of the external probe is represented by a gray box. The PGK-hygromycin cassette is inserted in the opposite transcriptional orientation and replaces a BamHI (B) fragment of exon 9 and intron 10. (B) Representative genomic blot probed with the external probe. A wild-type 4.5 kb and a recombined 3.7 kb fragment are shown. Mice were identified as wild-type (+/+), heterozygous (+/–) or homozygous mutant (–/–). (C) PARP-2 is not expressed in cells isolated from the testis of parp-2–/– mice. (D) Northern blot analysis of total RNA from testis using a 820 bp EcoRI fragment of parp-2 cDNA as a probe. Note that the expression of the RNase P RNA is not influenced by the parp-2 disruption.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.