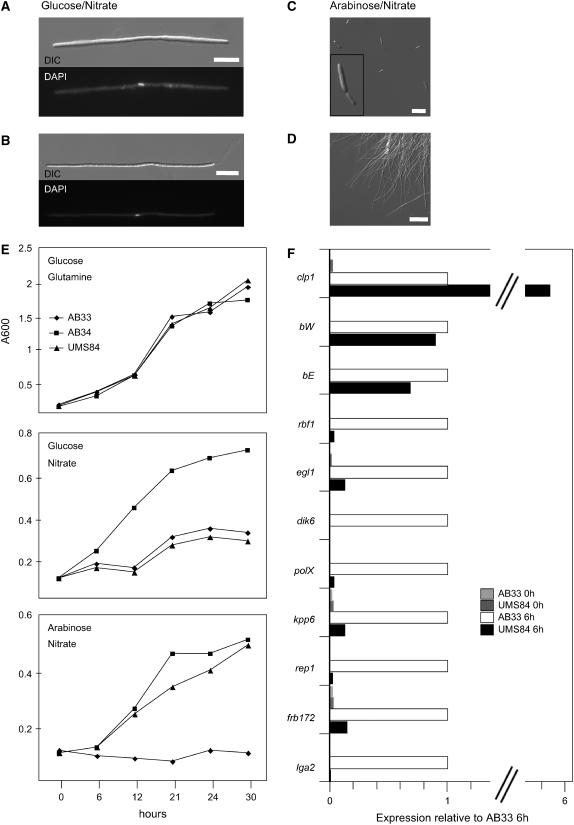
Figure 7.
clp1 Overexpression Inhibits b-Dependent Gene Regulation.
(A) to (D) Strains AB33 (a1 bE1nar1P/bW2nar1P), AB34 (a1 bE2nar1P/bW2nar1P), and UMS84 (a1 bE1nar1P/bW2nar1Pclp1crg1) were grown in minimal medium with Gln and glucose to an OD600 of 0.1 prior to induction. Expression of the b-genes was induced by nitrate, and clp1 expression was induced by arabinose. Induction of the active bE1/bW2 combination in strains UMS84 (A) and AB33 (B) leads to the formation of filaments with single nuclei (DAPI stain, bottom panel). Simultaneous induction of clp1 in strain UMS84 suppresses filamentation; the cells display a yeast-like phenotype (C). Strain AB33 is filamentous under identical conditions (D). DIC, differential interference contrast. Bars = 10 μm in (A), (B), and (D) and 20 μm in (C).
(E) Growth curves of strains AB33, AB34, and UMS84. Top panel: In medium containing glucose (clp1-off) and Gln (b-off), all strains display a similar growth curve. Middle panel: In medium containing nitrate (b-on) and glucose (clp1-off), strains AB33 and UMS84, both harboring the compatible bE1/bW2 combination, are drastically reduced in growth compared with strain AB34 harboring the incompatible bE2/bW2 combination. Bottom panel: In medium containing nitrate (b-on) and arabinose (clp1-on in strain UMS84), the growth rate of AB34 and UMS84 are comparable, despite the compatible bE1/bW2 combination in strain UMS84.
(F) Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of b-dependently expressed genes. Strains AB33 and UMS84 were shifted to arabinose/nitrate medium to induce the bE1/bW2 genes and additionally in UMS84 the clp1 gene. RNA was extracted before the shift (0 h) and 6 h after induction. Differences in expression of the monitored genes were calculated relative to the expression in AB33 6 h after induction of b (defined as 100%). Values were normalized to the expression of the constitutively expressed ppi gene. Given are the mean values of two technical replicates that gave similar results. The expression of the following b-induced genes was monitored: lga2, a gene with unknown function involved in mitochondrial fragmentation (Romeis et al., 2000; Bortfeld et al., 2004); frb172, encoding a protein with similarities to K+/H+ antiporters (Brachmann et al., 2001); rep1, encoding a hydrophobic surface protein (Wösten et al., 1996); kpp6, encoding a mitogen-activated protein kinase involved in appressoria formation (Brachmann et al., 2003); polX, encoding a protein with weak similarities to polymerase X (Brachmann et al., 2001); dik6, encoding a seven–transmembrane domain protein with unknown functions (Bohlmann et al., 1994; G. Weinzierl and J. Kämper, unpublished data); egl1, encoding a cellulase (Schauwecker et al., 1995); and rbf1, encoding a zinc finger transcription factor (M. Scherer and J. Kämper, unpublished data).