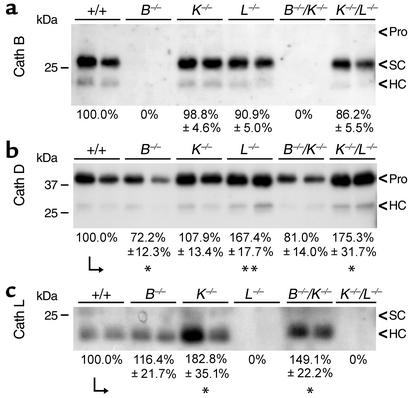
Figure 4.
Compensatory effects on the levels of cathepsin expression. Lysates of thyroids from mice of the indicated genotypes were normalized to equal amounts of protein, separated on 15% SDS gels, and transferred to nitrocellulose for subsequent incubation of the blots with antibodies against cathepsin (Cath) B (a), D (b), or L (c). Three to four blots each were used for densitometric evaluation as a measure of cathepsin expression levels. Levels are indicated by numbers below representative immunoblots and are expressed as the mean percentages ± SE of 100% expression in WT controls. Molecular mass markers are indicated in the left margins. Note that cathepsin B expression was absent from cathepsin B–/– and B–/–/K–/– thyroids, as expected, and that it was not altered by cathepsin K, L, or K/L deficiencies (a). In contrast, cathepsin D was downregulated in cathepsin B–/– thyroids, but upregulated under conditions of cathepsin L or K/L deficiency, whereas it was not significantly altered in cathepsin K–/– or B–/–/K–/– thyroids (b). Cathepsin L was absent from thyroid lysates of cathepsin L–/– or K–/–/L–/– mice, unaltered in cathepsin B–/– thyroids, and significantly upregulated in cathepsin K–/– or B–/–/K–/– mice (c). SC, single chain; HC, heavy chain; pro, proform. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.