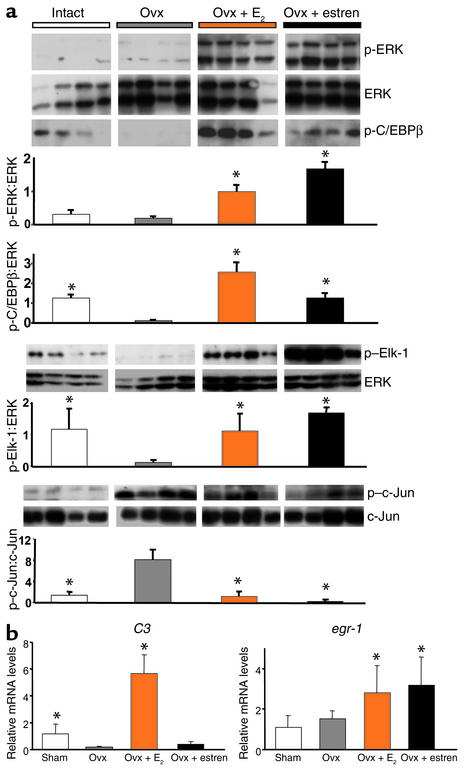
Figure 5.
E2 and estren induce phosphorylation of ERKs and their downstream targets, C/EBPβ and Elk-1, and suppress c-Jun activity in vivo. Ten-week-old Swiss Webster mice were ovx, left untreated for 5 days, and then implanted with 21-day slow-release pellets containing E2 (0.01 mg) or estren (2.6 mg) (a). Forty-eight hours later, ERK, C/EBPβ, Elk-1, and c-Jun phosphorylation was determined in L5 vertebrae; each lane represents one mouse. In a separate experiment, 6-month-old Swiss Webster mice were sham-operated or ovx. The ovx animals were then left untreated or implanted immediately with 60-day slow-release pellets containing E2 (0.025 mg) or estren (7.6 mg) (b). Six weeks later, total RNA from uteri (n = 4) was isolated. C3 and egr-1 expression was quantified by real-time PCR. Bars indicate means ± SD of triplicate determinations. *P < 0.05 versus ovx by ANOVA.