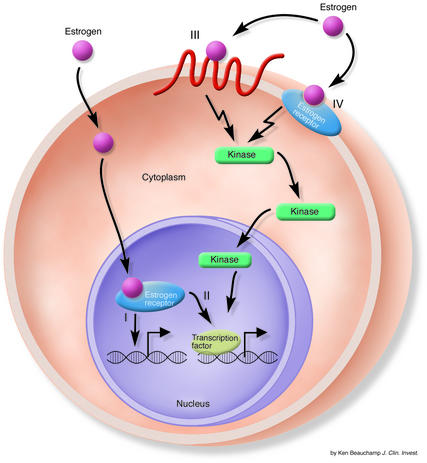
Figure 1.
Sex steroid hormones can affect cellular function by a variety of mechanisms. The illustration depicts the mechanisms by which estrogen influences cells. The classical pathways (I and II) depend on direct interaction of estrogen with its receptor in the nucleus. Once activated, the estrogen-receptor complex can directly mediate gene transcription (I) or interact with transcription factors (II) to influence their activity. The nonclassical pathways (III and IV) work more rapidly and depend on the ability of estrogen to interact with either nonsteroid hormone receptors (III) or steroid hormone receptors in the membrane (IV). Both nonclassical pathways activate kinases that ultimately regulate transcription of specific genes. Adapted from ref. 16.