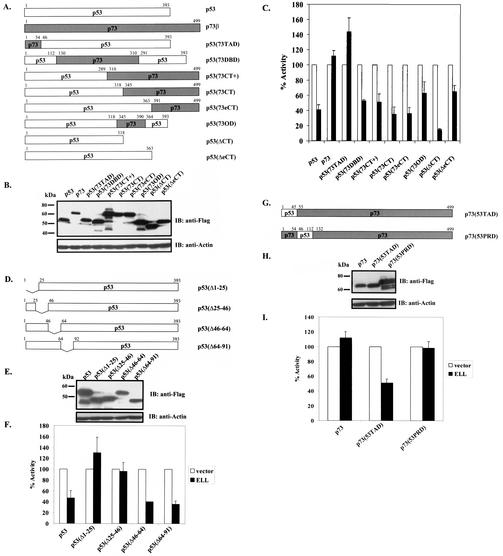
FIG. 2.
p53 (aa 1 to 45) is necessary and sufficient to render p53 sensitive to the inhibition by ELL. (A) p53/p73 chimeras were generated by using two-step PCR. p53 deletion mutants were PCR amplified with specific primers. (B) Protein expression of all constructs was verified by a anti-Flag Western blot of 293T-cell lysates transfected with 5 μg of each cDNA. Actin served as an equal loading control. (C) Chimeric or deletion mutants (1 μg) were cotransfected into p53−/− H1299 cells by calcium phosphate precipitation with either Flag-ELL (1 μg) (▪) or with empty vector (□) and with PG13 and pRL-TK plasmids. The relative luciferase activity measured 36 h posttransfection was set to 100% for every construct in the presence of vector alone. All transfections were repeated at least three times, in duplicate experiments (mean ± the SD). (D) Systematic 25-aa deletions in p53(NT) were generated by using standard PCR. (E) Protein expression of p53 deletions was confirmed by a Western blot with anti-Flag antibody. (F) The transcriptional activity of p53 deletion constructs in the presence of vector alone or Flag-ELL was assayed 36 h posttransfection as described in the text. The relative luciferase activity in the presence of vector was set at 100%. All transfections were repeated at least three times, with each done in duplicate (mean ± the SD). (G and H) Protein expression of the indicated p73/p53 chimeric constructs (G) was confirmed by Western blot with anti-Flag (H), and their transcriptional activity was measured by cotransfecting in the presence of either vector alone or Flag-ELL in H1299 cells. (I) The mean ± the SD of three separate transfections, each done in duplicate, is shown.