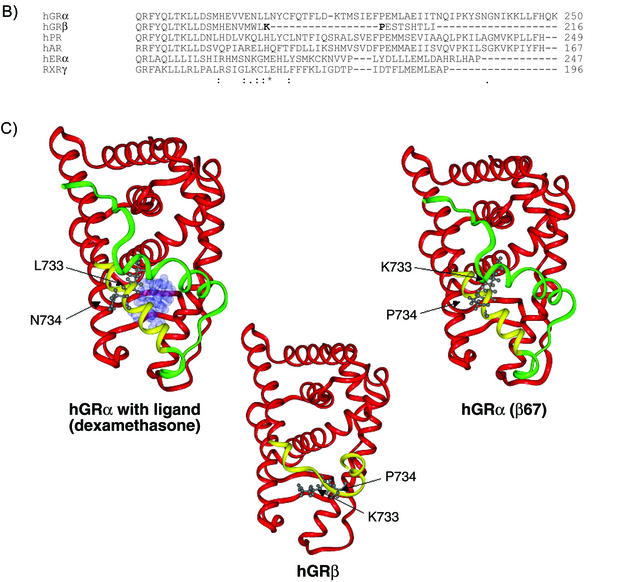
FIG. 8.
Structure predictions and molecular modeling. (A) A total of 12 secondary structure algorithms were run on the entire sequences of hGRα, hGRβ, hGRα(β6-7), and hGRα(1-742). The single-letter amino acid abbreviation for each receptor from residue 701 until the end is shown at the top of each sequence prediction block. Below the wt hGRα sequence is a comparison with the hPR. Below the hPR is the actual secondary structure found for the crystallographic solution of the hPR structure. The solid lines between hGR and hPR indicate a conserved amino acid. (B) Multiple sequence alignment of hGRα, hGRβ, and several other related receptors (hPR, hAR, hERα, and RXRγ). Alignment of hGRβ was done using the program Clustal W. Symbols underneath alignment indicate conserved residues. C) Three-dimensional models of hGRα, hGRβ, and hGRα(β6-7). Modeling was done using Molecular Simulations software. The common helices of each model (residues 525 to 727) are shown in red, the nonhomologous region from amino acid 728 through 742 is colored yellow, and the H12 region (residues 743 to 777), present in hGRα and hGRα(β6,7), is colored green. The hGRα model is shown with ligand occupying the binding pocket. The images also show the side chain orientations of residues 733 and 734 in each molecule.