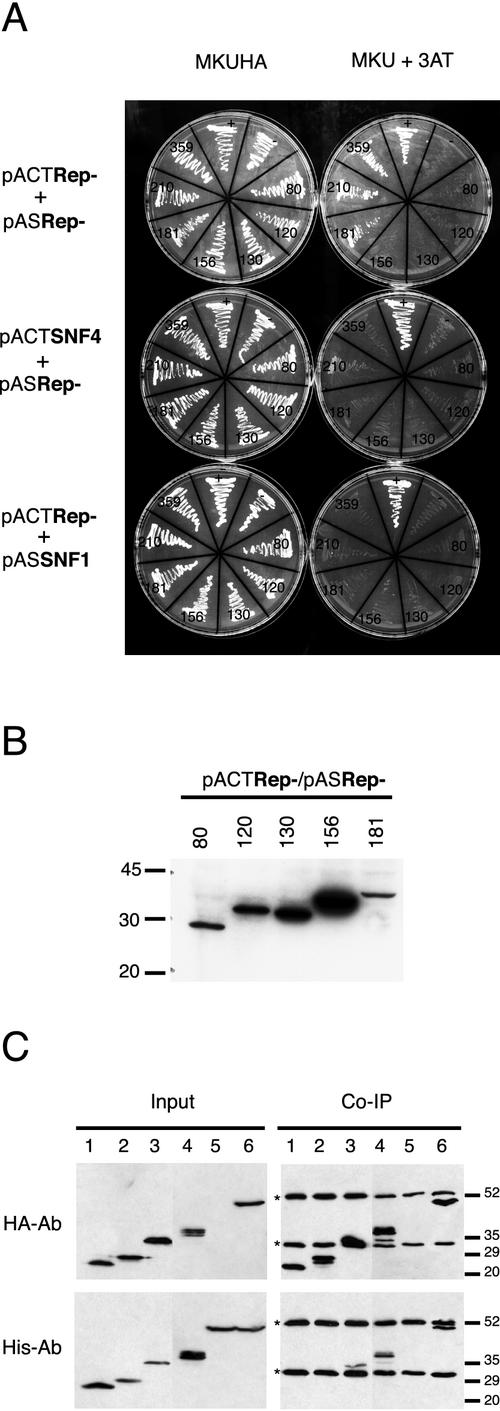
FIG. 2.
Rep-181 is the shortest self-interacting mutant. (A) Testing interaction in S. cerevisiae THS. Growth of strain PJ69-4A cotransformed with the plasmids indicated on the left, in medium selecting for the presence of plasmids (MKUHA [left]) or selecting for the interaction of expressed proteins (MKU + 3AT [right]), is shown. Symbols on plates: −, negative control strain coexpressing AgT and lamin; +, positive control strain coexpressing SNF1 and SNF4. Numbers indicate the number of N-terminal amino acids of each Rep protein. The TYLCSV wild-type Rep protein is 359 amino acids in length. (B) Western blot of protein extracts from S. cerevisiae coexpressing the GAL4 activation domain (AD)- and GAL4 binding domain (BD)-fused Rep proteins as indicated above each lane. The primary antibody was a monoclonal anti-GAL4 binding domain antibody. Migration of molecular mass markers is indicated on the left. (C) Testing interaction in vitro by coimmunoprecipitation. Western blots of total protein extracts from S. pombe coexpressing the HIS-tagged and HA-tagged Rep proteins are shown. Extracts were loaded on SDS-PAGE gel directly (Input) or after immunoprecipitation with anti-HA monoclonal antibodies (Co-Ip). The primary antibody (HA-Ab, monoclonal antibody against HA; His-Ab, monoclonal antibody against His) used in Western blotting is shown to the left. Lanes: 1, HIS-Rep130+HA-Rep130; 2, HIS-Rep156+HA-Rep156; 3, HIS-Rep181+HA-Rep181; 4, HIS-Rep210+HA-Rep210; 5, HIS-Rep; 6, HIS-Rep+HA-Rep. Molecular mass markers are indicated on the right. Asterisks mark the subunits of mouse IgG.