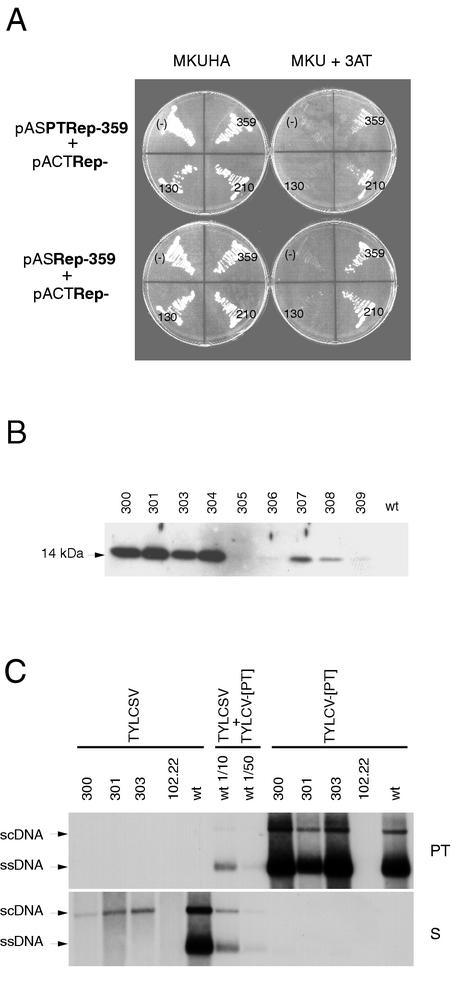
FIG. 5.
The oligomerization domain is required for the inhibition of TYLCV-[PT] replication. (A) Testing interaction in the S. cerevisiae THS. Growth of PJ69-4A strain cotransformed with plasmids indicated on the left in medium selecting for the presence of plasmids (MKUHA, left) or selecting for the interaction of expressed proteins (MKU + 3AT, right). On the plates, (−) indicates the control strain coexpressing SNF4 and either TYLCV-[PT] Rep or TYLCSV Rep, and the numbers indicate the number of N-terminal amino acids of each TYLCSV Rep protein. The TYLCSV wild-type Rep protein is 359 amino acids in length. (B) Western blot analysis of protein extracts from wild-type (wt) or transgenic (no. 300 to 309) N. benthamiana plants transformed with pTOM130. Primary antibody was a rabbit polyclonal anti-TYLCSV Rep antibody. (C) Southern blot analysis of TNA extracts from wild-type (wt) or transgenic N. benthamiana protoplasts expressing Rep-130 (lines 300, 301, and 303) or Rep-210 (line 102.22) transfected with infectious clones of TYLCSV or TYLCV-[PT], as indicated. The values 1/10 and 1/50 indicate the dilution factors of loaded samples. The blot was probed with a digoxigenin-labeled TYLCSV Rep-210 sense RNA probe (S) and reprobed with a digoxigenin-labeled TYLCV-[PT] V1 antisense RNA probe (PT).