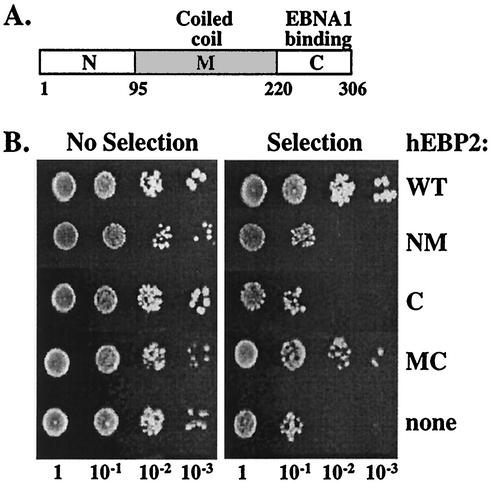
FIG. 3.
Human EBP2 domains required for EBNA1-mediated plasmid segregation. (A) Schematic representation of human EBP2 (hEBP2), showing the N-terminal (N), middle coiled-coil (M), and C-terminal (C) domains. Amino acid numbers are indicated. (B) Assays of loss of plasmid YRp7FR conducted in the presence of EBNA1 and either full-length human EBP2 (wt), human EBP2 residues 1 to 220 (NM), human EBP2 residues 220 to 306 (C), human EBP2 residues 95 to 306 (MC), or no human EBP2 (none). After 11 generations in the absence of selection for YRp7FR, serially diluted cultures were plated on selective and nonselective plates for YRp7FR.