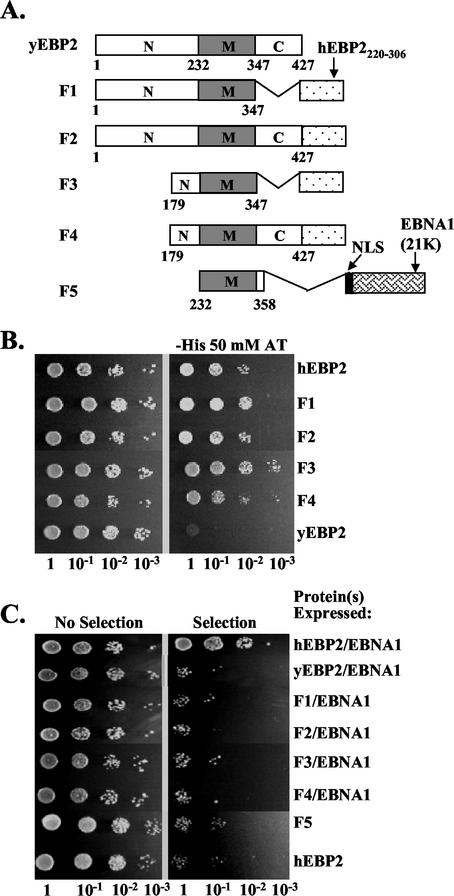
FIG. 7.
Plasmid segregation assays with yeast EBP2 fusion proteins. (A) Schematic representation of yeast EBP2 (yEBP2) and yeast EBP2-based fusion proteins (F1 to F5). The middle region (M) of yeast EBP2 corresponds to human EBP2 (hEBP2) residues 95 to 220. F2, F1, F3, and F4 are fusion proteins containing full-length yeast EBP2 or yeast EBP2 amino acids 1 to 347, 179 to 347, and 179 to 427, respectively, fused to the EBNA1-binding domain of human EBP2 (hEBP2220-306). F5 contains the middle region of yeast EBP2 (residues 232 to 358) fused to an NLS and the 21K fragment of EBNA1. (B) The ability of human EBP2 (positive control), yeast EBP2 (negative control), and EBP2 fusion proteins F1 through F4 to bind EBNA1 was determined in a yeast two-hybrid assay, where activation of a HIS3 reporter gene indicated an interaction. Dilutions of the two-hybrid assay cultures were grown on plates containing histidine (left panel) or lacking histidine and containing 50 mM aminotriazole (right panel). (C) Plasmid loss assays as described for Fig. 3 were conducted to determine the loss of YRp7FR in the presence of EBNA1 and human EBP2, yeast EBP2, or EBP2 fusion proteins F1 to F4. YRp7FR plasmid loss assays are also shown for F5 and human EBP2 alone.