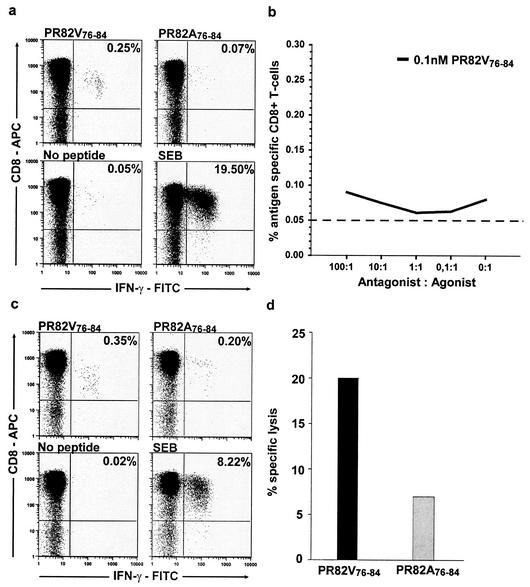
FIG. 3.
Antigen-specific CTL for the epitope PR82V76-84 do not recognize and kill targets presenting the mutant PR82A76-84 peptide. (a) In four out of the seven HLA-A2-positive subjects who remained wild type at position 82 (V82V), antigen-specific responses detected by CFC were only seen to the wild-type peptide PR82V76-84 but not to the PR82A76-84 mutant peptide, as illustrated with data from patient 3011. (b) To investigate if the PR82A76-84 mutant had antagonist properties, PBMC were stimulated with a suboptimal concentration (0.1 nM) of the agonist peptide (wild-type PR82V76-84) in the absence or presence of antagonist peptide (mutant PR82A76-84) in the CFC assay. The dashed line corresponds to the cutoff of the assay (mean background plus 2 standard deviations = 0.05). (c) In the three remaining patients, who were wild type at position 82 (V82V), reactivity was detected to the mutant PR82A76-84 but was always of a lower magnitude than to the wild-type peptide PR82V76-84, as illustrated in patient 3156. (d) In one of the patients, number 3156, with a reactivity to both peptides, CTL specific for the wild-type (PR82V76-84) epitope were not able to recognize and kill target cells presenting the mutant (PR82A76-84) epitope and thus confirmed that the V82A mutation induces viral escape from wild-type-specific CTL.