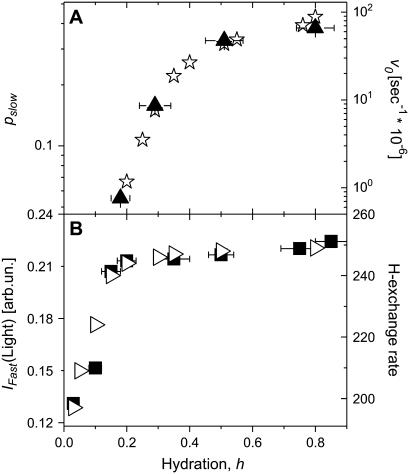
FIGURE 14.
(A) Parallel comparison of hydration dependences of the mobile fraction of hydrogen atoms involved in the slow relaxation process (▴) and enzymatic reaction rate, v0, of the lysozyme to hexasaccharide of N-acetylglucosamine ((GlcNAc)6) (⋆) as estimated by Rupley and colleagues (5,74). (B) Parallel comparison of hydration dependences of the integrated QES intensity of the fast process (▪) and hydrogen exchange rate (▹) in units of moles of exchanged H atoms/1 mol of lysozyme/24 h as estimated in Schinkel et al. (36). (T = 295 K).