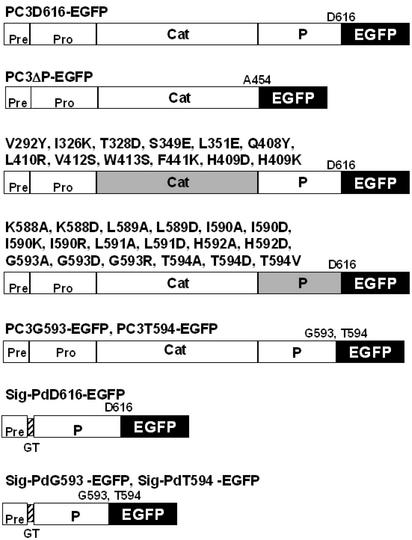
Figure 1.
Constructs of EGFP fusion and mutant proteins used in this study. Full-length or WT PC3 consists of a signal peptide (Pre) and four domains, pro-region (Pro), catalytic domain (Cat), P domain (P), and C-terminal domain. PC3–Asp-616 (PC3D616) is a C-terminally truncated active form of full-length PC3 (amino acids 1–736 of PC3) (38); PC3D616–EGFP is PC3D616-tagged with EGFP (black) via linkage at the N terminus of EGFP and was used as a fully active control in this study. PC3ΔP–EGFP is a P domain deleted (PC3 amino acids 1–453) EGFP-tagged control. Gray-shaded regions represent domains containing point mutations. PC3G593–EGFP and PC3T594–EGFP contain P domains, truncated after G593 or T594, respectively. Sig–PdD616–EGFP consists of a signal peptide (amino acids 1–27), followed by the P domain (amino acids 454–616) tagged with EGFP. In Sig–PdD616–EGFP, the signal peptide and P domain are linked by two added amino acids, glycine (G) and threonine (T). The signal cleavage site was predicted to lie between A27 and G28 in the VKAGTDPR sequence by the SIGNAL P V2.0 server (41, 42). Sig–PdG593–EGFP and Sig–PdT594–EGFP consist of signal peptide, truncated P domain at G593 or T594, respectively, and EGFP.