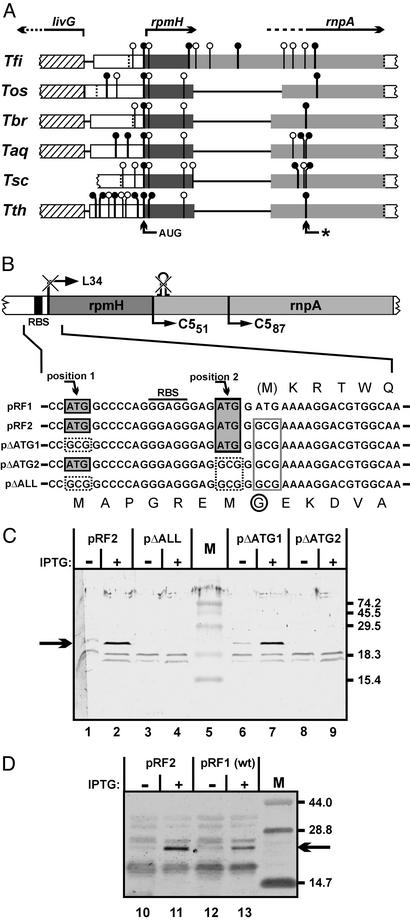
Figure 3.
(A) Alignment of rpmH–rnpA coding regions from different Thermus species. Start codons [vertical lines with circles; ●, commonly used codons (AUG and GUG); ○, rarely used codons (U/CUG, AUC/U)], and stop codons (dotted vertical lines) downstream of livG in the rnpA reading frames of six different members of the genus Thermus are indicated. Genes livG, rpmH, and rnpA and their direction of transcription are indicated at the top. Lines connecting the boxes represent sequence gaps introduced by the alignment program (OMIGA 2.0, Accelrys, Cambridge, U.K.). The AUG codon found in all six species and the initially assumed rnpA start codon from T. thermophilus (*) are marked by arrows at the bottom. Tfi, T. filiformis; Tos, T. oshimai; Tbr, T. brockianus; Taq, T. aquaticus; Tsc, T. scotoductus. (B) Expression plasmids carrying the rpmH–rnpA genomic region of T. thermophilus under control of a T7 promoter; pRF1 represents the WT situation. (Upper) Schematic representation: the rpmH start codon and the hairpin structure eliminated and disrupted, respectively, in all shown constructs except for pRF1; also shown are the native RBS and the N termini of the truncated RNase P proteins C551 and C587. (Lower) Sequences surrounding the inactivated start codon of rpmH are shown in detail. Gray-shaded boxes: potential rnpA start codons in the WT sequence; dotted boxes: mutation of potential rnpA start codons to GCG; box outlined in gray: mutated rpmH start codon. The amino acid sequences corresponding to the L34 and C5 reading frames are shown above and below the nucleotide sequences, respectively. M indicates the methionine start codon of L34 mutated in all constructs except for pRF1; the encircled G indicates the substitution of Gly for Asp resulting from mutation of the rpmH start codon. (C) Detection of a polypeptide with an apparent size of 22 kDa (arrow on the left) by Western blotting using the C587-specific antiserum before (−) and after (+) induction of transcription by T7 RNA polymerase from the four plasmids in E. coli BL21(DE3) host cells. M, marker proteins with sizes (in kDa) indicated on the right. IPTG, isopropyl β-d-thiogalactoside. (D) Attenuated expression of C51 in E. coli cells harboring plasmid pRF1 versus pRF2; for details, see legend to C.